Periodic Trends
90 likes | 214 Vues
This chapter delves into the periodic trends of elements, focusing on the distinct characteristics of metals and nonmetals. It explores the locations of these elements on the periodic table, their physical properties (luster, malleability, ductility), and their behavior as conductors or insulators. The discussion includes how metals lose electrons to form cations while nonmetals gain electrons to form anions. Key concepts such as atomic size, ionization energy, and electronegativity are defined and illustrated through trends down a family and across a period.

Periodic Trends
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Periodic Trends CP Chemistry Chapter 11
Metals • Location … • Characteristics … • Luster • Malleable & ductile • Conductors of heat & electricity • Lose electrons “cation” (positive)
Nonmetals • Location … • Characteristics … • Dull • Brittle • Insulators • Gain electrons “anions” (negative)
Reactivity • Definition: how quickly an element reacts with another. • Metals … • Down a family • Across a period • Sodium Disaster Clip • Sodium/Potassium Clip • Nonmetals … • Down a family • Across a period
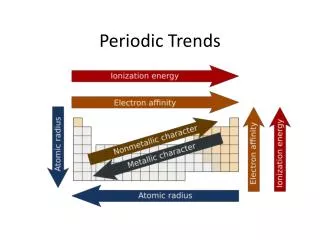
Atomic Size • Definition: the size of the atom • Down a family … • Across a period …
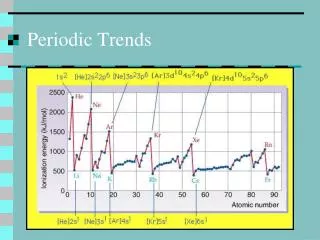
Ionization Energy • Definition: the energy required to remove an electron. • Down a family … • Across a period …
Multiple Ionization Energies • Definition: the energy needed to remove successive electrons. • Example: (all values in KJ/mole) • Mg 1st - 735 2nd -1445 3rd -7730 • Al 1st -580 2nd -1815 3rd - 2740 4th – 11,600
Electronegativity • Definition: the relative ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons to itself. • Down a family … • Across a period …