Understanding Income and Consumption Relationships in GDP and Disposable Income
60 likes | 168 Vues
This text explores the intricate relationships between income, consumption, and GDP, emphasizing the importance of disposable income. It highlights the formulas for calculating disposable income (DI) and consumption (C) in relation to net taxes and GDP. Furthermore, key concepts such as average and marginal propensities to consume and save are discussed, providing a comprehensive overview of economic behaviors concerning income and consumption. Understanding these relationships aids in economic forecasting and policy formulation.

Understanding Income and Consumption Relationships in GDP and Disposable Income
E N D
Presentation Transcript
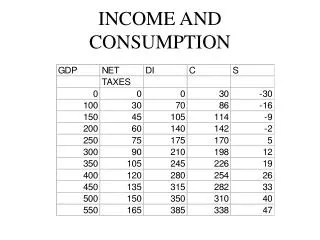
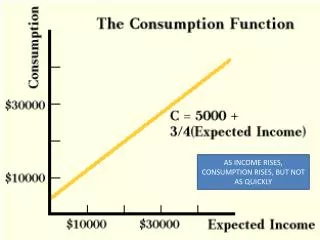
RELATIONSHIPS • GDP * .3 = net taxes • Disposable Income = GDP - net taxes • DI = GDP - .3* GDP • Consumption = 30 + .8 *DI • C = 30 + .8 *(GDP - .3*GDP) • C=30+.8*(1-.3)*GDP = 30 + .56 GDP • Savings = DI - C • Savings = -30 + .2 *DI