Virus
290 likes | 828 Vues
Virus. Warm-up. What is a pathogen? What is a virus? What is a viroid? What is a prion?. Virus. Virus Infectious particle made only of DNA or RNA and surrounded by a protein coat virus comes from Latin “poison” living? or non-living? rabies virus. Virus. Viroid

Virus
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Warm-up • What is a pathogen? • What is a virus? • What is a viroid? • What is a prion?
Virus Virus • Infectious particle made only of DNA or RNA and surrounded by a protein coat • virus comes from Latin “poison” • living? or non-living? rabies virus
Virus Viroid • Infectious particles that cause disease in plants • Single stranded RNA that does not have a protein coat • Passed through seeds or pollen • Stunt growth of plant
Virus Prion • Infectious particle made only of protein • Causes other proteins to fold incorrectly • Infectious but have no genetic material • No immune response • Example: Mad Cow Disease
Virus Virus First virus • Wendell Stanley (1935) • studying splotchy leaves on tobacco • discovered and isolated tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)
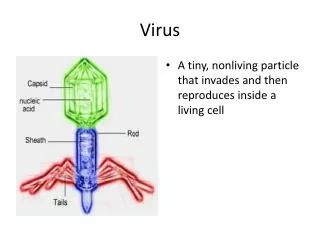
Virus Structure of a Virus • nucleic acid core (DNA or RNA), surrounded by outer protein coat called a capsid • different shapes: hellical (rod), sperical, polyhedral, different sizes 17nm – 100nm • some have an envelope with spikes that surrounds the capsid • contain no cell organelles, carry out no metabolic reactions • reproduce only inside a host cell • many are host specific • classified by type of nucleic acid and shape
Virus Structure of a Virus • nucleic acid core (DNA or RNA), surrounded by outer protein coat called a capsid
Virus Structure of a Virus • different shapes: hellical (rod), sperical, polyhedral, different sizes 17nm – 100nm
Virus Structure of a Virus • some have an envelope with spikes that surrounds the capsid HIV
Virus Structure of a Virus • many are host specific • ex: bacteriophage only infects bacteria
Virus Structure of a Virus • contain. . . no cell organelles, • carry out. . . no metabolic reactions • reproduce. . . only inside a host cell
Virus Structure of a Virus • classified by type of nucleic acid and shape
Structure of a Virusclassified by type of nucleic acid and shape
Virus Viral Reproduction Lytic Cycle (DNA virus) • virus takes over host cell, replicates, and destroys host cell • Steps • attachment • entry • replication • formation & assembly • lysis & release
Virus Viral Reproduction Lytic Cycle (DNA virus) • viruses use nucleotides, ribosomes, tRNA, and amino acids of host cell • viruses that undergo the lytic cycle are called virulent – short incubation time rhino virus
Virus Viral Reproduction Lytic Cycle (DNA virus)
Virus Viral Reproduction RNA virus Lytic cycle Steps • (almost the same as DNA virus) • attachment • entry • replication • replication of viral RNA • formation & assembly • lysis & release
Virus Viral Reproduction Lysogenic Cycle (DNA virus) • virus invades cell and becomes part of its DNA for a time • Steps • attachment • entry • intergration • viral DNA breaks open host cell DNA and joins with it forming a provirus • cell division • host cell divides, produces 2 new host cells with the provirus inside
Virus Viral Reproduction Lysogenic Cycle (DNA virus) • provirus may: • change phenotype of host • prevent other viruses from entering host • pull out of host DNA & enter lytic cycle
Virus Viral Reproduction Lysogenic Cycle (DNA virus) • viruses that go through lysogenic cycle are temperate viruses – long incubation period herpes simplex
Virus Viral Reproduction Lysogenic Cycle (DNA virus)
Virus Viral Reproduction Lysogenic Cycle (DNA virus)
Virus Viral Reproduction RNA virus Lysogenic cycle Steps • inject viral RNA into host • viral RNA makes a DNA copy using reverse transcriptase • DNA strand replicates and enters host DNA to become a provirus
Virus Viral Reproduction RNA virus Lysogenic cycle • RNA viruses that go through the lysogenic cycle are called retroviruses HIV
Virus Treating Viruses vaccine • injection of weakened or killed viruses Jonas Salk (1955) • developed first vaccine for the polio virus
Virus Other Viruses polio
Virus Other Viruses measles
Virus Other Viruses smallpox