Functional Group Interconversion by Nucleophilic Substitution.
390 likes | 1.55k Vues
Outline. Alcohols to Alkylating AgentsSulfonate EstersHalidesIntro. Of Functional Groups at Saturated CarbonSolvent effects (Nudity)NitrilesAzidesOxygen NucleophilesNitrogen NucleophilesSulfurPhosphorus. Outline Continued. Cleavage of C-O bonds in ethers and estersInterconversion of CO-X

Functional Group Interconversion by Nucleophilic Substitution.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
1. Functional Group Interconversion by Nucleophilic Substitution. Chapter 3
2. Outline Alcohols to Alkylating Agents
Sulfonate Esters
Halides
Intro. Of Functional Groups at Saturated Carbon
Solvent effects (Nudity)
Nitriles
Azides
Oxygen Nucleophiles
Nitrogen Nucleophiles
Sulfur
Phosphorus
3. Outline Continued Cleavage of C-O bonds in ethers and esters
Interconversion of CO-X Derivatives
Prep. For Acylation CO-halide
Prep for Esters
Prep for Amides
Problems:
1, 4, & 5
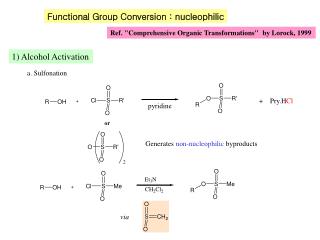
4. Conversion of Alcohols to Alkylating Agents Sulfonate Esters
Toluenesulfonate (tosylate) Me-Ph-SO2-
From Tosyl-Cl, needs base to buffer
Methanesulfonate (mesylate) Me-SO2-
From Mes-Cl
Often trifluoroderivative, better leaving group.
CF3-SO2-Cl
All react with alcohols
Need base to buffer and aprotic solvents
5. Thionyl Chloride (SOCl2)
Through chlorosulfite RO-SO-Cl
Inversion of configuration � SN2
Xanthate
ROH + Base (NaH) + CS2 + Me-I
RO-CS-CMe then SO2Cl2 to R-Cl
Retention of config., two SN2
Xanthates big in cellulose chemistry.
Conversion of Alcohols to Alkylating Agents - Halides
6. Conversion of Alcohols to Alkylating Agents � Halides II From Phosphate esters
Some rearrangement
Must be an acid stabile compound
Ph3P + CCl4 to give Ph3P+CCl3 Cl-
Forms Phosphite esters and Cl- attacks
7. Examples
9. Substitution General Solvent effects
Leaving group reactivity
RSO3- > I- > Br- > Cl-
Hydrocarbons, halogenated Hydrocarbons, and ethers unsuitable
Acetone and MeCN fair
DMSO, DMF, HMPA and alcohols better suited
Phase Transfer
Quaternary ammonium salts; 2 liquid phases
Crown for nudity, look over reference 32 in book
10. Cleavage of C-O bond in Ethers and Esters HX, X= I, Br, Cl, F blunt force where milder conditions needed
Usually activation to a C-X bond then substitution
Examples 1-3 in Scheme 3.2 for �CN substitutions
Examples 4-7 for Azides (NaN3)
Examples 8 & 9 Amine
Example 10, Oxygen alkylation from Enamine
Williamson ether synthesis for 13-16
Diazoalkanes for fun, #17.
Carboxylates as the nucleophile 18-20
11. Scheme 3.2 #�s 1-3
14. Hydrolysis
15. Ethers by Base Cata. Alkylation
16. Esterfication
17. Phosphorus and Sulfur
18. Kaboom!!!
19. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives SOCl2 with RCO-OH to RCO-Cl
RCO-Cl
Reacts with all Nucleophiles to give Derivatives
RNH2, RR�NH, RCO-O-OCR, ROH, RSH, RSeH, etc.
Cleavages:
Ethers to alcohols
BBr3, BF3, BF3�Et2O, Me3SiI, and rest in Scheme 3.3
Esters to other esters
Me3SiCl/NaI + RCO-OR� to silyl ester
21. To �Acylation� Compounds Formation of RCO-Cl (Br)
Highly reactive to form all RCO-Z compounds
Acyl-pyridinum highly reactive Enhances rate
As well as 4-N,N-dimethylaminopyridine
Increases nucleophilicity and bacisity
Enhances rate 104
3� and hindered alcohols accomplished
Anhydrides + MgBr2 + hindered amine
Diisopropylethylamine
1,2,2,6,6-pentamethylpiperdine
Lanthanide triflates (M(OSO2CF3)3 mild for 3�
Sc, Lu, Yb
22. More Acylation Cata. Me3Si-OSO2CF3 good for 3�
Inert solvent
Active agent; O-Si of the anhydride
Tributyl phosphine + Anhydride via acyl phosphonium ion Bu3P+-COR
Ph3P + NBS give RCO-Br
Ph3P + RCO-OH gives RCO-OPPh3
Carbonyldiimiazole gives Amide + CO2
DCC(dicyclohexylcarbodiimide) used in polypeptide synthesis.
23. Examples
24. Esters RCO-Cl (Br also) + Alcohol choice
RCO-OH + Alcohol and H+ cata.
Fischer Rx.
Needs drying force,
Azeotrope
Getter solids
Anhydrides third choice
25. Amides CO-Halide or Anhydride plus amine in water
Schotten-Bauman
DCC, for in situ generation CO-OH + Amine
NO2-C6H4- and 2,4,5-trichloro-C6H2- for peptide activation
N-hydrosuccinimides activator (also esters)
BOP-Cl (picture)
Aluminum Amides Al2O3 final product
26. Problems Chapter 3 # 1, 4 & 5