Tracing the Katrina Disaster: Challenges in Emergency Response
210 likes | 286 Vues
Explore the failures in emergency planning during Hurricane Katrina aftermath and the implications for local, state, and federal agencies. Learn about the complexities of federalism and the struggle between state and national powers. Discuss the principles of federalism, state sovereignty, and national supremacy that shaped responses to the disaster.

Tracing the Katrina Disaster: Challenges in Emergency Response
E N D
Presentation Transcript
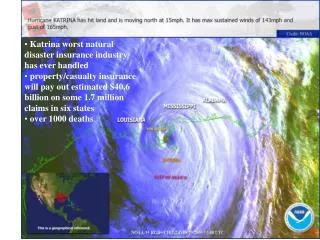
Tracing the Katrina Disaster “Local, state and federal emergency agencies had been planning for years how to respond before and after this kind of emergency. They even had practice drills where every kind of relief issue was reviewed -- food, water, security and health -- and who was responsible for delivering those services was specifically laid out in numerous plans. But many of those plans fell apart in Katrina's aftermath. Despite warnings of a worst-case scenario, bureaucratic wrangles prevented soldiers from getting to the scene, the plan for emergency communications left police in the dark and helpless, and truckloads of emergency supplies ended up hundreds of miles away. Four days after Katrina hit, it was still unclear who was in charge of the relief effort” In a special report on All Things Considered, NPR's Laura Sullivan and Daniel Zwerdling examine how the disaster called Hurricane Katrina unfolded. MORE: Katrina: What Went Wrong? 4:58 p.m. EDT | Sept. 9, 2005 |
Central Govt States States Citizens Citizens What is it?
Why Important? Decentralizes Politics Decentralizes Our Policies Fed Govts.- Canada, India, Germany, US Unitary Govts.- France, Britain, Italy
Federalism v. Unitary • Federalism- political system with local government units, as well as the national government, that can make final decisions regarding some governmental activities and whose existence is protected. • Unitary-all local govts. Subservient to national govt., local govts., can be altered or abolished, local govts. have no final authority over any significant govt. activities.
I’ll give $20 to the first person to find the word federalism in the Constitution It Is absent but State and National Power clearly defined in Article 1, Section 9 and 10
NATIONAL • NATIONAL • BOTH • NATIONAL • STATE • STATE • STATE • BOTH State or National Power? Declare War Coin Money Tax Regulate commerce w/ foreign nations and among states Conduct elections Ratify amendments Regulate Commerce w/in a state Take private property for public purposes, w/ just compensation Dual Federalism- both supreme in their own sphere.
V. Who wins?????
Advocates of a strong national govt say….. Supremacy Clause! but…..This Constitution, and the Laws of the United States which shall be made in Pursuance thereof; and all Treaties made, or which shall be made, under the Authority of the United States, shall be the supreme Law of the Land; and the Judges in every State shall be bound thereby, any Thing in the Constitution or Laws of any State to the Contrary notwithstanding.
10th Amendment Advocates of state’s rights believe this means the national govt has only those powers specifically assigned by the constitution
Establishing National Supremacy 1) Implied Powers: McCulloch v. Maryland Elastic Clause- “necessary and proper” -Could Congress charter a national bank? Yes, even though not explicitly explained in Constitution -Could states tax the federal bank? No, national powers were supreme and therefore immune to state challenge
Establishing State Sovereignty Supreme Court Strengthens States’ rights- U.S. v. Lopez-guns in school Printz v United States –background checks on gun purchasers -also strengthened 11th Amendment protecting states from suits by citizens of other states or foreign nations
Establishing National Supremacy 3) Civil War: -Struggle over not just slavery but between states and national govt -Settles the “Nullification” question Do states have the right to “nullify” the Constitution”?
Establishing National Supremacy -Grants in aid- categorical and block -Mandates- Civil Rights, Environmental Protection, No Child Left Behind
Yes, Full Faith and Credit Clause • No, Full Faith and Credit Clause • Article IV Sec. 1 • Defense of Marriage Act? What would MI do???? Jack and Jill got married in Maine and moved to Michigan for the weather. Are they still married? Susie gets her driving license in Texas. Can she get pulled over in MI for not having a MI license?
Return him to Indiana….. • Extradition • Article IV Sec. 2 What would MI do???? John Dillinger is fleeing Wisconsin after robbing banks and has made it down South to MI. The officials know where he his.
Yes, Privileges and Immunities • Article IV Sec. 2 What should Sam do???? Sam is visiting PA from MI and has to pay 9% sales tax (he’s not to happy since MI is only 6%….). Does he have to pay?
Article IV…. Federalism ALSO involves relationships among states
Cooperative: • Share responsibilities for public policy • Marble Cake Analogy • Mingled resp. and blurred distinctions • Historically starts w/ New Deal, Great Society • Involve shared costs, federal guidelines, shared administration Dual v Cooperative Dual: Pre national govt. dominance Each remain supreme w/in their own spheres Layer Cake Analogy Powers of National Govt. interpreted narrowly
A Devolution Revolution? -returning power to the states? -do we cut entitlements?