lim increasing
10 likes | 186 Vues
3 L. 3 cos - sin . lim increasing. lim increasing. 1 - lim / . . . max (, ) =. H lim - ( lim - ). 1 - lim / H ( lim ). IMPROVED WINDOWING FUNCTIONS FOR SYNTHETIC APERTURE IMAGING RADIOMETERS

lim increasing
E N D
Presentation Transcript
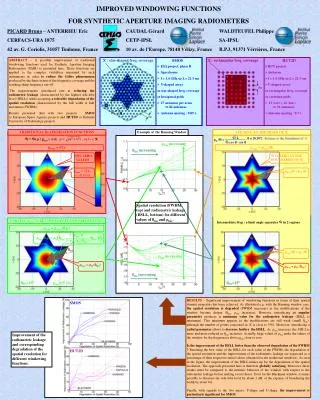
3 L 3 cos - sin lim increasing lim increasing 1 - lim/ max(,)= Hlim- (lim- ) 1-lim/H(lim) IMPROVED WINDOWING FUNCTIONS FOR SYNTHETIC APERTURE IMAGING RADIOMETERS PICARD Bruno – ANTERRIEU Eric CAUDAL Gérard WALDTEUFEL Philippe CERFACS-URA 1875 CETP-IPSL SA-IPSL 42 av. G. Coriolis, 31057 Toulouse, France 10 av. de l’Europe, 78140 Vélizy, France B.P.3, 91371 Vérrières, France ABSTRACT –A possible improvement of traditional windowing functions used for Synthetic Aperture Imaging Radiometers (SAIR) is presented here. These functions are applied to the complex visibilities measured by such instruments in order to reduce the Gibbs phenomenon produced by the finite extent of the frequency coverage and the resulting sharp frequency cut-off. The improvements introduced aim at reducing the radiometric leakage (characterized by the highest side-lobe level (HSLL)) while accepting a tolerable degradation of the spatial resolution (characterized by the full width at half maximum (FWHM)). Results presented deal with two projects : SMOS (a European Space Agency project) and HUT2D (a Helsinki University of Technology project). H : star-shaped freq. coverage • ESA project, phase B • Spaceborne • f = 1.4 GHz = 21.3 cm • Y-shaped array star-shaped freq. coverage hexagonal grids • 27 antennae per arms82 antennae • Antenna spacing : 0.89 λ SMOS H : rectangular freq. coverage • HUT project • Airborne • f = 1.4 GHz = 21.3 cm • U-shaped array • rectangular freq. coverage • cartesian grids • 13 (vert.), 12 (hor.)36 antennae • Antenna spacing : 0.7 λ HUT2D u u Example of the Hanning Window STICKING TO THE SHAPE OF H TRADITIONAL 2D APODIZATION FUNCTIONS , [0,30°]:distance to the boundaries of H Ŵ = Ŵ( / max ) with , (u,v) H H()= lim increasing max = Cte max = max() NON ZERO VALUES Ŵ IS ZERO AT THE BOUNDARIES OF H Ŵ Ŵ max()=H() max = √3 L (~ 47 [u]) Spatial resolution (FWHM, top) and radiometric leakage (HSLL, bottom) for different values of lim and lim . FORCING max TO BE CONSTANT AT LOW FREQUENCIES Intermediate Step : a limit angle separates Ŵ in 2 regions max= max (,) Ŵ lim lim max()=H () lim increasing lim max= H (lim) max = H (lim) lim=15° lim=15 [u] lim=15° RESULTS –Significant improvement of windowing functions in terms of their spatial domain properties has been achieved. As illustrated e.g. with the Hanning window case, the spatial resolution is degraded (FWHM increases) as the modifications of the window become deeper (lim, lim increases). However, introducing an angular parameter produces a minimum value for the radiometric leakage (HSLL is minimum). This minimum appears as the modifications are still weak (small lim), although the number of points concerned in H is close to 50%. Moreover, introducing a radial parameter allows to decrease further the HSLL. As lim increases, the HSLL is more and more reduced as limincreases. Actually, large values of lim make the values of the window for the frequencies above lim close to zero. Is the improvement of the HSLL better than the observed degradation of the FWHM ? Retaining the best value of the HSLL for each value of the FWHM, the degradation of the spatial resolution and the improvement of the radiometric leakage are expressed as a percentage of their respective initial values (obtained for the traditional windows). As seen in the figure, the improvement of the HSLL makes up for the degradation of the spatial resolution. The approach presented here is therefore globally satisfying. Moreover, these results must be compared to the intrinsic behavior of the window with respect to the radiometric leakage before making a real choice.Even for the Blackman window, it seems possible to decrease the side-lobe level by about 2 dB, at the expanse of broadening the width by about 6%. Finally, with regards to the two arrays, Y-shape and U-shape, the improvement is particularly significant for SMOS. SMOS Improvement of the radiometric leakage and corresponding degradation of the spatial resolution for different windowing functions. HUT2D