Understanding Metamorphic Rocks: Formation and Textures
150 likes | 316 Vues
Metamorphic rocks undergo significant changes in structure, texture, and mineral composition due to the effects of heat, pressure, and fluids deep within the Earth. This process, known as metamorphism, can occur under varying temperature ranges (50ºC to over 1000ºC) and typically takes place over 2 km beneath the surface. There are two main types of metamorphism: contact and regional. Metamorphic rocks can be categorized into foliated and nonfoliated textures, influenced by the arrangement of mineral grains and the presence of specific minerals known as index minerals.

Understanding Metamorphic Rocks: Formation and Textures
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Metamorphic Rocks Ch 4 S4
Introduction • Rocks can go through process of metamorphism • Metamorphism: a change in the constitution of rock; specifically: a pronounced change effected by pressure, heat, and water that results in a more compact and more highly crystalline condition • Metamorphic rocks are rocks in which the structure, texture, or composition has been changed • Can be changed by heat, pressure, or both
Origins of Metamorphic Rock • Texture/mineral composition can change (∆) when surroundings change (∆) • Occurs between 50ºC & 1,000ºC • Can occur over 1000ºC • Metamorphic change takes place more than 2 km beneath the surface of the Earth
Contact Metamorphism • Occurs near igneous intrusions • Occurs near bodies of magma • Rock is heated and changed by the nearby magma
Regional Metamorphism • Occurs when pressure builds up in rock buried under other rock formations or when Earth’s crust collides • Occurs over thousands of km3 within the rocks crust • Found beneath continental rock formations
Composition of Metamorphic Rock • Metamorphism occurs when temperature & pressure inside the Earth’s crust change • Minerals change into different minerals that are more stable in the new environment • Index minerals: minerals that form only at certain temperatures & pressures • Used to measure temperature, depth, & pressure at which a rock undergoes metamorphosis • Include: biotite mica, chlorite, and garnet
Textures of Metamorphic Rock • 2 textures • Foliated • Nonfoliated
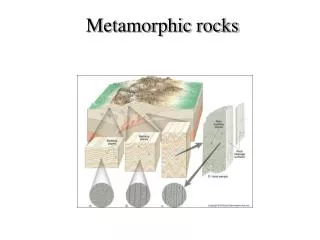
Foliated Metamorphic Rock • Texture: mineral grains are arranged in planes or bands • Contains aligned grains of flat minerals • Diagram shows a sedimentary rock transforming via metamorphism
Nonfoliated Metamorphic Rock • Texture: mineral grains are not arranged in planes or bands • Made of one or only a few minerals • Mineral crystals may change in size or mineral may change in composition
Metamorphic Rock Structures • Deformation: a change in the shape of a rock due to a force placed on it • Rock may be squeezed or stretched • Bends in the rock are indicators