Understanding DNA Replication Process
100 likes | 196 Vues
Learn about the steps involved in DNA replication, enzymes required, importance of base pairing, and how genetic information is preserved. Explore key terms such as helicase, DNA polymerase, nucleotides, and base pairing.

Understanding DNA Replication Process
E N D
Presentation Transcript
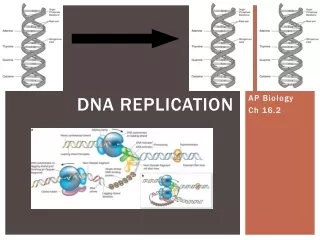
Step 1:Special enzymes unwind & “unzip” the DNA molecule into 2 strands.
Step 2:The strands separate so each strand can be a template for making another strand.
Step 3:2 new strands are formed using the rules of base pairing (A-T, C-G). Nucleotides are added in opposite directions.
Enzymes Involved • Helicase • Unzips the two strands and holds them apart during replication • DNA Polymerase • Links the nucleotides to form the new strands of DNA • Proofreads each new strand of DNA
Original strand New strand DNA polymerase Growth DNA polymerase Growth Nitrogenous bases New strand Original strand DNA Replication
ComparingDNA Replication Cytoplasm Nucleus S phase S phase So daughter cells have the same genetic information Start at 1 point, moves in both directions Starts at 100’s of points, moves in both directions.
Review • Why is DNA replication needed? • When does DNA replication occur? • How many strands are there in a DNA molecule? • What are the three structures that make up a nucleotide? • What is the importance of base pairing? • When during DNA replication are enzymes used? • DNA replication results in ____ DNA molecules, each with one ______ strand and one _______ strand. • What happens to the two new DNA molecules?
Answers to Review • So each daughter cell gets the same genetic info. • S phase of interphase • Two strands • A sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, & a nitrogenous base (A, T, G, or C) • So each strand can be used as a template • HelicaseUnzips strands & holds them apart DNA polymerase Joins new nucleotides & proofreads • DNA replication results in two DNA molecules, each with one old strand and one new strand. • They separate during anaphase and enter two different cells.