Language and the brain
420 likes | 1.43k Vues
Language and the brain. Introduction to Linguistics. Language + brain =. The brain http://www.g2conline.org/2022. Physical features of the brain. Language centers. Language centers. Producing a spoken word. Hearing a word. Reading a word. How the brain works.

Language and the brain
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Language and the brain Introduction to Linguistics
How the brain works • The brain is composed of neurons. • Neurons are the basic units of information processing in the nervous system. • There are about 10 billion interconnected neurons.
Split brain experiments • The two hemispheres of the brain is connected by corpus callosum. • The function of corpus callosum • To commute the info between the two sides of the brain.
What would happen if corpus callosum is cut? • Play the split brain experiments game at http://nobelprize.org/educational_games/medicine/split-brain/index.html
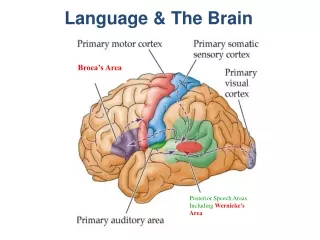
Aphasia • A language disorder produced by brain damage • Major types • Broca’s aphasia • Wernike’s aphasia
Broca’s aphasia (Expressive aphasia) • Symptoms • Unable to express themselves by more than a single word at a time • Content words are ok; function words are not • “Yes... ah... Monday... er... Dad and Peter H... and Dad.... er... hospital... and ah... Wednesday... Wednesday, nine o'clock... and oh... Thursday... ten o'clock, ah doctors... two... an' doctors... and er... teeth... yah’” • Damaged area • The front regions of the left hemisphere
Wernike’s aphasia • Symptoms • Fluent speech with no informational value • Comprehension is impaired. • “I called my mother on the television and did not understand the door. It was too breakfast, but they came from far to near. My mother is not too old for me to be young.” • Damaged area • Temporal lobe of the left hemisphere
Broca’s aphasia Prevents a person from producing speech Person can understand language Words are not properly formed Speech is slow and slurred. Wernicke’s aphasia Loss of the ability to understand language Person can speak clearly but the words that are put together make no sense. Broca vs. Wernicke
Conduction aphasia • No connection between Broca’s area and Wernike’s area • Symptoms • Be able to understand and produce speech, but cannot repeat what they have just heard.
Dyslexia • Dyslexia • The impairment of reading ability • Symptoms • Problems with spelling • Reading difficulties • Difficulties in recognizing individual sounds in words • Difficulties in naming things. • Problems organizing in the right order
Brain plasticity • The ability of the brain to reorganize the neural pathways based on new experiences. • The environment plays an important role. • The implications on learning?