AP Lang: Test Prep BW
280 likes | 611 Vues
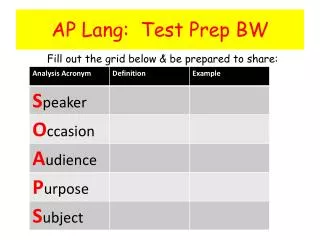
AP Lang: Test Prep BW. Fill out the grid below & be prepared to share:. Meaning: . 30-15-10 List. Examples: Artifact facsimile. Root: Fac , fact. Class Examples: . Visual/Memory Clue. Meaning: . Meaning: . Examples: dialogue biology. Examples:

AP Lang: Test Prep BW
E N D
Presentation Transcript
AP Lang: Test Prep BW Fill out the grid below & be prepared to share:
Meaning: 30-15-10 List Examples: Artifact facsimile Root: Fac, fact Class Examples: Visual/Memory Clue
Meaning: Meaning: Examples: dialogue biology Examples: Autograph graphic Root: Graph Root: Log Class Examples: Class Examples: Visual/Memory Clue Visual/Memory Clue
Meaning: Meaning: Examples: Transcribe subsrciption Examples: Mortal mortician Root: Mort Root: Scrib script Class Examples: Class Examples: Visual/Memory Clue Visual/Memory Clue
Analyzing a Text: AP Lang Style Three things you must know in order to accurately analyze a text: 1) SOAPS Rhetorical Strategies a. Appeals (logos, pathos, ethos) b. Style (diction, imagery, details, syntax, tone….DIDST) These Questions: a. HOW do the RS help the author achieve his/her purpose? b. WHY does the author chose those strategies for that particular audience and for that particular occasion? Without this, you are merely summarizing the text!
Introduction (aka “rhetorical precis”) FORMAT: Essential Information for Intro: Speaker, Occasion, & Subject 1) (Writer’s Credentials), (writer’s first and last name), in his/her (type of text), (title of text), (strong verb), (writer’s subject). Purpose (Writer’s last name)’s purpose is to (what the writer does in the text). Audience 3) He/she adopts a (adjective describing the attitude/feeling conveyed by the writer) tone in order to (verb phrase describing what the writer wants reader to do/think) in his/her (intended audience).
Intro Rhetorical Precis: Novelist Amy Tan, in her narrative essay, “Fish Cheeks,” recounts an embarrassing Christmas Eve dinner when she was 14 years old. Tan’s purpose is to convey the idea that, at fourteen, she wasn’t able to recognize the love her mother had for her or the sacrifices she made. She adopts a sentimental tone in order to appeal to similar feelings and experiences in her adult audience. Speaker, Occasion, & Subject 1) (Writer’s Credentials), (writer’s first and last name), in his/her (type of text), (title of text), (strong verb), (writer’s subject). Purpose (Writer’s last name)’s purpose is to (what the writer does in the text). Audience 3) He/she adopts a (adjective describing the attitude/feeling conveyed by the writer) tone in order to (verb phrase describing what the writer wants reader to do/think) in his/her (intended audience).
“Flamingo” Intro Rhetorical Precis: Speaker, Occasion, & Subject 1) (Writer’s Credentials), (writer’s first and last name), in his/her (type of text), (title of text), (strong verb), (writer’s subject). Purpose (Writer’s last name)’s purpose is to (what the writer does in the text). Audience 3) He/she adopts a (adjective describing the attitude/feeling conveyed by the writer) tone in order to (verb phrase describing what the writer wants reader to do/think) in his/her (intended audience).
“Challenger” Intro Rhetorical Precis: Speaker, Occasion, & Subject 1) (Writer’s Credentials), (writer’s first and last name), in his/her (type of text), (title of text), (strong verb), (writer’s subject). Purpose (Writer’s last name)’s purpose is to (what the writer does in the text). Audience 3) He/she adopts a (adjective describing the attitude/feeling conveyed by the writer) tone in order to (verb phrase describing what the writer wants reader to do/think) in his/her (intended audience).
Tuesday AP Lang: Test Prep BW Scheme: a pattern of words or sentence construction used for rhetorical effect (syntax) Trope: the use of language in a non-literal way; aka figure of speech (diction) Schemes Tropes List all the schemes & tropes you already know!
The Glass Castle • Parts 1-4 Quiz…open note/open book • Scene Swap! Due on Tuesday… • Part 5: Due on 4/23
Thursday AP Lang: Test Prep BW Fill out the grid below & be prepared to share:
Analyzing a Text: AP Lang Style Three things you must know in order to accurately analyze a text: 1) SOAPS Rhetorical Strategies a. Appeals (logos, pathos, ethos) b. Style (diction, imagery, details, syntax, tone….DIDST) These Questions: a. HOW do the RS help the author achieve his/her purpose? b. WHY does the author chose those strategies for that particular audience and for that particular occasion? Without this, you are merely summarizing the text!
Rhetorical Strategies a. Appeals (logos, pathos, ethos) b. Style (diction, imagery, details, syntax, tone….DIDST)
“The Plastic Pink Flamingo: A Natural History” (Jennifer Price)
“Speech on the Challenger Disaster” (Ronald Reagan, 1/28/86)
Body: The Analysis…work chronologically… 1) Sentence one: Identify section of text & main idea of section (Writer’s last name) (transition word) his/her (type of text) by (strong verb) that (main idea of that section). 2) Sentence two: Conveys the writer’s support for the main idea by identifying and providing a specific example for one rhetorical strategy used by the writer. (Repeat if you want to discuss more than one rhetorical strategy) 3) Sentence three: Explains how the rhetorical strategies you discussed in the previous sentences help the writer achieve his purpose by using and in order to statement. 4) Sentence four: Identifies the effect of the writer’s use of these rhetorical strategies on the audience.
“Challenger” body paragraph one: 1) Sentence one: Identify section of text & main idea of section (Writer’s last name) (transition word) his/her (type of text) by (strong verb) that (main idea of that section). 2) Sentence two: Conveys the writer’s support for the main idea by identifying and providing a specific example for one rhetorical strategy used by the writer. (Repeat if you want to discuss more than one rhetorical strategy) 3) Sentence three: Explains how the rhetorical strategies you discussed in the previous sentences help the writer achieve his purpose by using and in order to statement. 4) Sentence four: Identifies the effect of the writer’s use of these rhetorical strategies on the audience.
“Challenger” body paragraph one: Reagan begins his tribute to the Challenger astronauts by acknowledging that the shuttle accident has appropriately postponed his planned State of the Union address and by expressing the depth of his and his wife’s personal grief. He appeals to the mournful emotions of his audience by admitting that he and Nancy are “pained to the core” (3), that today is rightfully a “day for mourning and remembering”(2-3), and that the accident is “truly a national loss”(4). He joins in this time of mourning in order to unify the nation and humbly admit that “we share this pain with all of the people of our country”(4). The outpouring of emotion from the president conveys a calming tone that reassures the Nation that their grief is both understandable and proper. 1) Sentence one: Identify section of text & main idea of section (Writer’s last name) (transition word) his/her (type of text) by (strong verb) that (main idea of that section). 2) Sentence two: Conveys the writer’s support for the main idea by identifying and providing a specific example for one rhetorical strategy used by the writer. (Repeat if you want to discuss more than one rhetorical strategy) 3) Sentence three: Explains how the rhetorical strategies you discussed in the previous sentences help the writer achieve his purpose by using and in order to statement. 4) Sentence four: Identifies the effect of the writer’s use of these rhetorical strategies on the audience.
“Flamingo” body paragraph one: 1) Sentence one: Identify section of text & main idea of section (Writer’s last name) (transition word) his/her (type of text) by (strong verb) that (main idea of that section). 2) Sentence two: Conveys the writer’s support for the main idea by identifying and providing a specific example for one rhetorical strategy used by the writer. (Repeat if you want to discuss more than one rhetorical strategy) 3) Sentence three: Explains how the rhetorical strategies you discussed in the previous sentences help the writer achieve his purpose by using and in order to statement. 4) Sentence four: Identifies the effect of the writer’s use of these rhetorical strategies on the audience.
Your assignment: Finish the analysis of EITHER the Challenger speech or “Flamingo”; that is, write the 2nd & 3rd body paragraphs following the established outline. Do first: • Fill out DIDST grid labeled “Middle of Text” & “End of Text” for your chosen Text • Write the body paragraphs…preface with the intro paragraphs we wrote on Monday! • Turn-in