SORDOCEGUERA
140 likes | 739 Vues
SORDOCEGUERA. VARIABLES QUE INTERVIENEN. Repercusión de la sordera en el acceso al contexto. MOVILIDAD. ACCESO A LA INFORMACIÓN Y A LA CULTURA. OTROS PROBLEMAS. VELOCIDAD. CONECCIÓN CON EL MEDIO Y COMUNICACIÓN CON LOS DEMÁS. PÉRDIDA DE EXPRESIVIDAD. ÚNICO CANAL DE INFORMACIÓN.

SORDOCEGUERA
E N D
Presentation Transcript
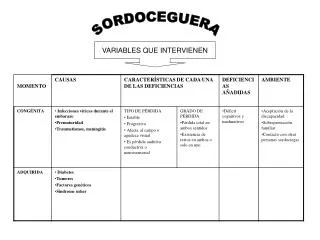
SORDOCEGUERA VARIABLES QUE INTERVIENEN
Repercusión de la sordera en el acceso al contexto MOVILIDAD ACCESO A LA INFORMACIÓN Y A LA CULTURA OTROS PROBLEMAS VELOCIDAD CONECCIÓN CON EL MEDIO Y COMUNICACIÓN CON LOS DEMÁS PÉRDIDA DE EXPRESIVIDAD ÚNICO CANAL DE INFORMACIÓN CONCENTRACIÓN Y CANSANCIO
RECURSOS INTERIORES Y EXTERIORES OLFATO TACTO DESARROLLO AL MÁXIMO DE LOS SENTIDOS OTROS SENTIDOS GUSTO
Gómez (2000), agrupa a la personas sordociegas atendiendo a dos variables
EL SINDROME USHER DEFINICIÓN enfermedad hereditaria que implica sordera asociada a una pérdida progresiva de visión, producida por Retinosis Pigmentaria • TIPO I • - Sordera neurosensorial congénita bilateral, no progresiva y simétrica, de profunda a severa • El aprendizaje de la lengua oral suele ser difícil • Dificultades en el equilibrio • La RP suele aparecer entre los 8 y 10 años • Es la más común • TIPO II • - Sordera congénita bilateral, no progresiva y simétrica, de leve a moderada (no se detecta hasta los 4 años) • Adquiere el lenguaje con audífonos • La RP suele aparecer entre los 20 años • TIPO III • - Sordera neurosensorial congénita progresiva, de leve a profunda • - La RP suele aparecer entre los 20 y 30 años • la RP y la sordera suelen aparecer al mismo tiempo
CARACTERÍSTICAS se puede manifestar de diferentes formas: VISIÓN BORROSA VISIÓN PERIFÉRICA Y NO CENTRAL VISIÓN CON MANCHAS VISIÓN EN TÚNEL VISIÓN PARCIAL
CARACTERÍSTICAS • La velocidad del deterioro de la visión es variable • No se suelen convertir en ciegos totales • La afectación visual es más grave en el T.I • Movilidad independiente • MANIFESTACIONES OCULARES COMUNES • Ceguera nocturna • Reducción periférica del campo de visión • Pérdida de agudeza central • Deslumbramiento inhabitual
SINDROME DE WOLFRAN O DIMOAD • MANIFESTACIONES OCULARES COMUNES • ATROFIA ÓPTICA BILATERAL, NORMALMENTE SIMÉTRICA • EDAD DE COMIENZO ENTRE LOS 2 Y LOS 24 AÑOS • MANIFESTACIONES AUDITIVAS COMUNES • sordera bilateral y simétrica y progresiva que va de suave a moderada en la primera década de vida e intensa en la tercera década • Variedad en la edad de comienzo y del deterioro