Mass and Energy
90 likes | 228 Vues
This article explores the fundamental concepts of mass and energy in the context of special relativity, focusing on the beta factor and its significance when speeds approach that of light (v > 0.1c). The total energy is discussed in terms of kinetic energy, highlighting that at low velocities kinetic energy must be adjusted. Additionally, it covers rest energy, which solely depends on mass, devoid of velocity or potential energy. The article also provides practical examples, including the energy requirements of an average household and the acceleration of electrons in a potential.

Mass and Energy
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Beta Factor • Relativity matters when speeds are close to that of light. • v > 0.1c • v/c > 0.1 (less than 1% error) • The beta factor is often used in relativity to scale values according to the speed of light.
Total Energy • Total energy is based on kinetic energy. • No potential, only kinetic • Classically E = ½ mv2 • With relativity the total energy depends on β. • Check this definition at low speed. • Approximation: • Application:
Low Energy Match • To match kinetic energy with the result at low velocity, the extra term must be subtracted. • The kinetic energy also depends on β.
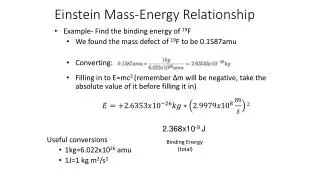
Rest Energy • The extra term for energy is still there when an object is at rest. • This energy only depends on the mass.
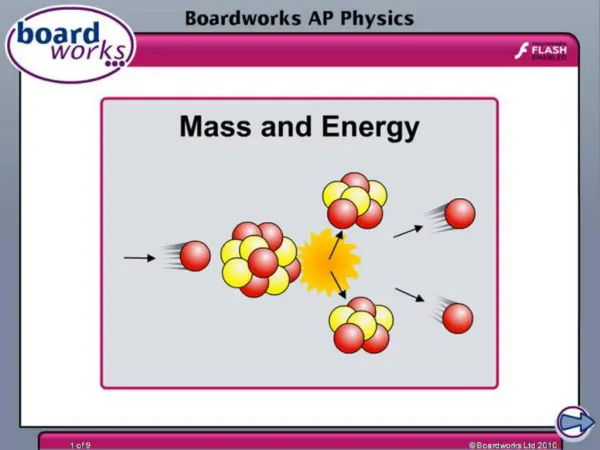
Energy from Mass • The rest energy exists in an object’s inertial frame. • No velocity • No potential • Just mass • Conservation of energy implies that this rest energy can be converted to other forms.
Hot House • An average house uses 2 x 1010 J for heating and cooling in one year. • What mass equivalent is that? • Solve for the rest mass. • Use c = 3 x 108 m/s. • m = 2 x 10-7 kg • About 1/10 the mass of a human hair
Electron Gun • An electron is accelerated through a potential of 106 V. • Rest energy 0.511 MeV • What is the final speed in units of c? • The rest energy doesn’t change. • Potential to kinetic • γ = 3.0, v = 0.94c