Consumer Behavior Family Decision Making
180 likes | 608 Vues
Consumer Behavior Family Decision Making. Shauna Heynen Vicky Shen. Table of Content. Introduction Family Decision Making Individual Decision Making Differences Similarities Marketing to Families Conclusion. Introduction. Every family is unique .

Consumer Behavior Family Decision Making
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Consumer BehaviorFamily Decision Making Shauna Heynen Vicky Shen
Table of Content • Introduction • Family Decision Making • Individual Decision Making • Differences • Similarities • Marketing to Families • Conclusion
Introduction • Every family is unique. • There is no decision that can work for all families. • It is important for marketers to know how families make consumer decisions.
Family Decision Making • Modern Family • The new meaning of household • Age of the family • Family size • Non-traditional family structures • The people living at home
Family Decision Making (cont.) • The Family Life Cycle Model (FLC) • Can provide a clear image of what the target market is to the marketers. • Examples: • on average younger households spend less money on products and services • new formed families without children are willing to spend more time and money on entertainment and social life
Family Decision Making (cont.) • Type of Decisions • Consensual purchase decision: • Members agree on desired purchase • Accommodative purchase decision: • Members have different preferences or priorities and cannot agree on a purchase
Families Decision Roles: Pre-purchase Stage: Initiator Information gatherer Gatekeeper Influencer Purchase Stage: Decision maker Preparer Buyer User Post-purchase Stage: Maintainer Disposer Family Decision Making (cont.)
Family Decision Making (cont.) • Decision Makers • Autonomic decision • When one family member chooses a product • Syncratic Decision • When the family jointly makes a decision • Four Factors Determine the Degree to Which Decisions will be Made Jointly by One or the Other Spouse • Sex-role stereotypes • Spousal resources • Experience • Socioeconomic Status
Individual Decision Making • Decision Making Process: • Need Recognition • Information Search • Evaluate the Alternative • Purchase Decision • Consumption and Learning
Individual Decision Making (cont.) • Types of Decisions:
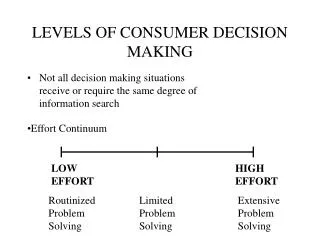
Differences Family Decision Making Individual Decision Making • More than one person will be participate in any stage of problem-solving sequence • 2 basic types of decisions: • Consensual purchase decision • Accommodative purchase decision • Individuals only have to make decisions for themselves • A continuum scaleis used to evaluate types of consumer decisions: • Habitual decision making • Limited problem solving • Extended problem solving
Similarities Family Decision Making Individual Decision Making • Same Decision Making Process: • Need Recognition • Information Search • Evaluate the Alternative • Purchase Decision • Consumption and Learning • Same Decision Making Process: • Need Recognition • Information Search • Evaluate the Alternative • Purchase Decision • Consumption and Learning
Marketing to Families • Marketers must attempt to create a need for a product for two or more people. • Use the Family Life Cycle • Discovering who the FFO is • Family Financial Officer • Children can be very influential on the products being consumed
Conclusion • Families are ever evolving unique groups containing two or more people • Tradition family to the Modern family • Marketers have developed certain criteria and tricks
References Solomon M. R., Zarichowsky J. L., Polegato R., (2005) Consumer Behavior 3rd Edition You Tube LLC, 2007,. (July 30,2007) http//:youtube.com
Family Decision Making Questions ?