Understanding Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
120 likes | 237 Vues
This resource teaches how to solve absolute value equations and inequalities. Learn the definition of absolute value, represented by |x|, indicating distance from zero on a number line. Explore methods to solve equations like ax + b = c, where c > 0, by setting up two separate equations. Understand the distinction between "and" and "or" problems when solving inequalities. Comprehensive examples and step-by-step guides are provided for clarity. Enhance your algebra skills and check your solutions effectively.

Understanding Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Learning Check • I can solve absolute value equation.
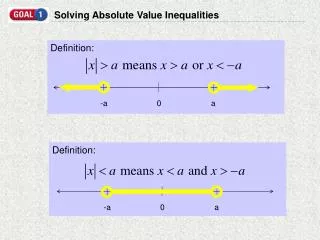
Absolute Value (of x) • Symbol lxl • The distance x is from 0 on the number line. • Always positive • Ex: l-3l=3 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2
Ex: x = 5 • What are the possible values of x? x = 5 or x = -5
To solve an absolute value equation: ax+b = c, where c>0 To solve, set up 2 new equations, then solve each equation. ax+b = c or ax+b = -c ** make sure the absolute value is by itself before you split to solve.
Ex: Solve 6x-3 = 15 6x-3 = 15 or 6x-3 = -15 6x = 18 or 6x = -12 x = 3 or x = -2 * Plug in answers to check your solutions!
Ex: Solve 2x + 7 -3 = 8 Get the abs. value part by itself first! 2x+7 = 11 Now split into 2 parts. 2x+7 = 11 or 2x+7 = -11 2x = 4 or 2x = -18 x = 2 or x = -9 Check the solutions.
Solving Absolute Value Inequalities • ax+b < c, where c>0 Becomes an “and” problem Changes to: –c<ax+b<c • ax+b > c, where c>0 Becomes an “or” problem Changes to: ax+b>c or ax+b<-c
Ex: Solve & graph. • Becomes an “and” problem -3 7 8
Solve & graph. • Get absolute value by itself first. • Becomes an “or” problem -2 3 4
Resource • http://www.taosschools.org/ths/Departments/MathDept/spitz/Courses/Algebra2/presentations.htm