CHAPTER 8: LEARNING Classical Conditioning
250 likes | 614 Vues
CHAPTER 8: LEARNING Classical Conditioning. Opening Experiment: Directions: Please place your head on desk, close your eyes and relax. This is NOT Hypnosis. Learning. YouTube - Scary Loud Noise Learning - a change in behavior due to experience

CHAPTER 8: LEARNING Classical Conditioning
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CHAPTER 8: LEARNING Classical Conditioning Opening Experiment: Directions: Please place your head on desk, close your eyes and relax. This is NOT Hypnosis
Learning • YouTube - Scary Loud Noise • Learning - a change in behavior due to experience • We are not born with a blueprint of how to survive, we learn by experience. We have adaptability – the capacity to cope with our changing environments.
Behaviorism • Behaviorism – • Psychology should be an objective science • Studies behavior without reference to mental processes . • RELATE EVERYTHING WE LEARN IN THE NEXT 2 CHAPTERS TO BEHAVIORISM aka Behavioral perspective
Behaviorists • Ivan Pavlov – Russian physiologist who observed conditioned salivary responses in dogs (1849-1936)
John B. Watson – American psychologist who established the psychological school of behaviorism. (1878 – 1958) "Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own specified world to bring them up in and I'll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select--doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant- chief, and yes, even beggarman and thief, regardless of his talents, penchants, tendencies, abilities, vocations, and race of his ancestors" Behaviorists
Behaviorists • B.F. Skinner – An American psychologist who advocated behaviorism and studied the effects of reinforcement. (1904 – 1990) (Operant Conditioning)
Associative Learning • Learning by association – learning that certain events occur together. • Classical Conditioning – learning the relationship between stimuli and responses. P. 314 Fig. 8.1 • Operant Conditioning – learning through rewards and punishments. P.315 Fig. 8.2 • Behavior followed by it’s consequences
Examples of Classical Conditioning • Alfred Hitchcock Films • YouTube - Top 5 Horror Movies theme songs • Jaws Theme Song • Bakeries • Songs • Sounds of the ocean CD • Your Dogs and Cats • Classical Conditioning with a Daisy the Cat • Classical Conditioning Experiment
Classical Conditioning • Classical conditioning – learning to associate neutral stimuli with stimuli that produce reflexive, involuntary responses, and will learn to respond similarly to the new stimulus as they did the old one.
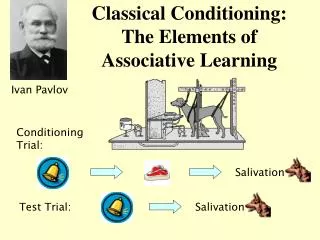
Pavlov’s Dog • Pavlov observed the salivation of dogs… • Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS-aka US) – something that elicits a natural response (FOOD) • Unconditioned Response (UCR- aka UR) – natural, involuntary response (SALIVATION) • Neutral Stimulus (NS) – something that does not elicit any particular behavior without conditioning (BELL)
Pavlov’s Dog UCS UCR NS No response CR
Pavlov’s Dog • Order of stimuli • Conditioned Stimulus / Neutral Stimulus (CS) presented first THEN the Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) • Present within a short amount of time from one another… half a second.
Pavlov’s Dog • After Conditioning …. • Conditioned Stimulus (CS) – a originally irrelevant stimulus that comes to trigger a particular behavior (BELL) • Conditioned Response (CR) – the learned response that initially occurred to the unconditioned stimulus and now occurs to the conditioned stimulus (SALIVATION) • Classical Conditioning - Ivan Pavlov – YouTube Two and Half Men - Pavlov's Bar – YouTube Interesting fact about Pavlov’s laboratory I read about
Pavlov’s Laboratory • ouTube - Baha Men - Who Let The Dogs Out (Original version) | Full HD | 1080p (:18)
Pavlov’s Dog • FOOD (UCS) ------------ SALIVATION (UCR) • BELL (NS) ------------ Initially produced no salivation • NS + UCS ----------------- SALIVATION (UCR) • BELL (CS) ---------------- SALIVATION (CR)
More Classical Conditioning • Practice Classical Conditioning Onion Breath. P.318 Fig. 8.4 romantic vs. sexual arousal • Classical conditioning and the blink response
Examples of Classical Conditioning • Classical Conditioning at BGSU – YouTube • The Office - Pavlov's dog on Vimeo • Classical Conditioning within Psychology - "Attack of the Quack" – • YouTubeClassical Conditioning in High School Clockwork Orange classical conditioning scene
5 concepts of classical conditioning • Acquisition- Learning has taken place when the animal/person responds to the conditioned stimulus. This initial learning is calledacquisition. (the animal has acquired a new behavior)
Extinction and Spontaneous Recovery • Will the CS always yield the CR… even if repeatedly presented without the UCS? • Extinction – the diminishing of an CR if the CS is not presented with the UCS • Will the CS yield a CR after a wait period? • Spontaneous recovery – the reappearance of an extinguished conditioned response after a rest period.
Distinguishing Between Stimuli • Will the animal respond to a somewhat varied stimulus? • Generalization – after conditioning, the tendency for a stimulus, similar to the CS, to evoke a similar response. P. 321 snails cartoon • Discrimination – the learned ability to distinguish between CS and another stimulus. • Water Bottle Experiment. • Rape as classical conditioning p. 325
Activity Classically Conditioning a Student • Directions: On a sheet of scrap paper write out the following 9 terms in one column • UCS, UCR, CS, CR, Acquisition, Extinction, Spontaneous Recovery, Generalization, Discrimination. • After I conduct the short demonstration label the 4 parts of the classical conditioning then explain WHEN in the experiment the last 5 terms took place or might have taken place.
John B. Watson’s Little Albert Experiment • Little Albert feared loud noises but not white rats. • Loud noise (UCS) – fear (UCR) • Presentation of rat (NS) – no fear • Pair rat (NS) and loud noise (UCS) – fear (UCR) • After several repetitions, the sight of the rat (CS) produced fear (CR) The Little Albert Experiment
Taste Aversions • Garcia and Koelling’s Experiment – Rats and taste aversions • Rats were given food, then given radiation, which led to nausea. Then the rats would later avoid that food. • 2 interesting findings: • Aversion developed to only tastes (not sights or sounds) • Even after hours had passed between presenting the CS and the UCS the aversion still developed. • Humans may experience taste aversions: • Eat food – become sick – Feel nauseas at the sight or smell of the food. • Sheep Coyotes and Ranchers poison in sheep carcass.
Human Taste Aversions • “secondary disgust”- Fudge (shape of muffins vs. droppings) • Favorite Soup: stirred in a thoroughly washed used flyswatter (82%) brand new flyswatter (58%) used comb that has been thoroughly washed (76%) served in thoroughly washed used dog bowl (71%)
Classical Conditioning facts • People with OCD and/or Autism are 3 times likely to be conditioned. • Men who saw a car with a seductive women were more likely to rate the car as faster, better designed and more appealing than men who viewed the same ad without. • Associating celebrities with products • Taking people to lunch/dinner to make business deals.