Dissolving of an Ionic Compound
320 likes | 920 Vues
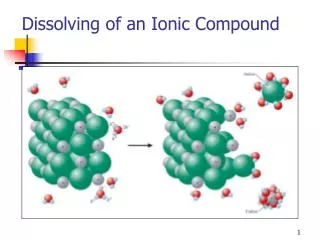
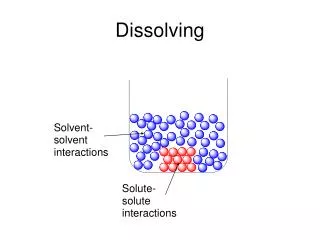
Dissolving of an Ionic Compound. Figure 7-2 p124. p129. Clicker Question. What are the possible products? AgNO 3( aq ) + KCl ( aq ) → ? A) AgCl and KNO 3 B) AgNO 3 and KCl C) AgK and NO 3 Cl D) Any of the above could be the products. p129. Solubility Rules. p130.

Dissolving of an Ionic Compound
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Clicker Question • What are the possible products? AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq)→ ? A) AgCl and KNO3 B) AgNO3 and KCl C) AgK and NO3Cl D) Any of the above could be the products.
Precipitation Reactions • Know how to use the solubility rules (you will be given them on the exam). • Know how to write equations from reactants (ionic reactants). • Understand what solutions “look” like at a very magnified level.
Clicker Question When aqueous AgNO3 and aqueous Na2CrO4 are mixed, what are the formulas of the products? A) Na2NO3 and AgCrO4 B) NaNO3 and Ag2CrO4 C) NaNO3 and AgCrO4 D) Na2NO3 and Ag2CrO4
Given: Na2CrO4(aq) + AgNO3(aq)→ Ag2CrO4 + NaNO3 Which is the solid? A) NaNO3 B) Ag2CrO4 Solubility Rules Most nitrate salts are soluble. Most salts of sodium, potassium, and ammonium cations are soluble. Most chloride salts are soluble. Exceptions: Ag+ and Pb2+. Most sulfate salts are soluble. Exceptions: Ca2+, Ba2+, and Pb2+. Most hydroxide salts are only slightly soluble. Soluble ones are: Na+, K+, and Ca2+. Most sulfide, carbonate, and phosphate salts are only slightly soluble. Clicker Question
Clicker Question Which solution is the most concentrated?
Solution Problem #1 • You have 1.00 mol of sugar in 125.0 mL of solution. Calculate the concentration in units of molarity.
Solution Problem #2 • You have a 2.50 M sugar solution. Calculate the number of moles of sugar in 300.0 mL of this solution.
Solution Problem #3 • You have a 10.0 M sugar solution. What volume of this solution do you need to have 2.00 mol of sugar?
Clicker Question You add 250.0 mL of water to 250.0 mL of a 4.00 M sugar solution. What will happen to the concentration? A) increase B) decrease C) stay the same
Solution Problem #4 You add 250.0 mL of water to 250.0 mL of a 4.00 M sugar solution. Calculate the concentration of the new solution in units of molarity. (Assume the volumes are additive.)
Solution Problem #5 • You dissolve 100.0 g of NaOH in 150.0 mL of solution. Determine the concentration of the solution in terms of molarity.
Solution Problem #6 • We have a 0.800 M solution of NaOH. You need 75.0 mL of a 0.35 M solution. How do you make such a solution?
Solution Problem #7 • Answer the following questions for 60.0 mL of 2.00 M calcium chloride solution. a) How many moles of calcium chloride are in solution? How many moles of chloride ions are in this same solution? b) You add 40.0 mL of water to the solution. How many moles of calcium chloride are in the new solution? c) What is the molarity of the new solution?