Tile Drainage
210 likes | 1.11k Vues
Tile Drainage. Precision Agriculture Soil 4213 Billie McKean April 27, 2007. Tile drainage. Tile drainage is a practice for removing excess water from the subsurface of soil intended for agriculture. Just the opposite of irrigation. History of Drainage Tile.

Tile Drainage
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Tile Drainage Precision Agriculture Soil 4213 Billie McKean April 27, 2007
Tile drainage • Tile drainage is a practice for removing excess water from the subsurface of soil intended for agriculture. • Just the opposite of irrigation.
History of Drainage Tile • Drainage tiles were described by Cato as early as 200 B.C. • First introduced to the United States in 1838 by John Johnson • He was a native of Scotland and practiced tiling on his farm in Seneca County, NY • He laid 72 miles worth of clay tile on 320 acres and increased his wheat yield from 12 bushels/acre to 60 bushels/acre
History of Tile Drainage • The Mike Weaver Drain Tile Museum in the home of John Johnston is comprised of a collection of over 500 drain tiles ranging from 500 B.C to plastic tiles of recent times
The Need for Drainage • Too much subsurface water can be counterproductive to agriculture by preventing root development, and inhibiting the growth of crops.
The Need for Drainage • Too much water can also limit access to the land, particularly by farm machinery • Operating machinery in excessively wet conditions may result in soil degradation due to excess soil compaction
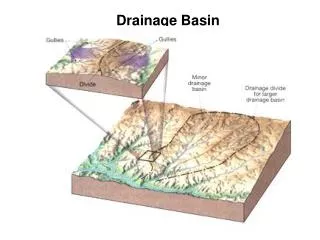
Plumbing of Drain Tile • A sort of “plumbing” is installed below the surface of agricultural fields, consisting of a network of below-ground pipes that allow subsurface water to move out from between soil particles and into the tile line. • Ultimately, the water is deposited into lakes, streams, and rivers located at lower elevations.
Plumbing of Drainage Tile • Water enters the tile line either through the gaps between tile sections, in the case of older tile designs or through small perforations in modern plastic tile.
Positive Impacts of Drainage • Helps soils warm up and dry out faster in the spring • Allows earlier field operations to occur • Increased crop yields • Reduces year to year variability in crop yields • More crop uniformity • Helps to bring soil moisture levels down to levels optimum for crop growth • Reduces sediment and phosphorous losses
Negative Impacts of Drainage • Increase nitrate-nitrogen losses • Contributes to hypoxia in coastal ecosystems • Potentially contaminates surface water sources (fertilizers, eroded soil, agrochemicals, and other agricultural run-off pollutants) • Associated with loss of wetlands
References • http://d-outlet.coafes.umn.due • http://www.fws.gov.midwest/EcosystemConservation/water_issues.html • http://www.agry.purdue.edu/water/fieldstn-WQFS.htm • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tile_drainage • http://www.omafra.gov.on.ca/english/engineer/facts/01-063.htm. • http://www.genevahistoricalsociety.com/Johnston.htm