### Understanding Coordinate Geometry: Key Concepts and Applications ###
160 likes | 272 Vues
Explore the fundamental concepts of coordinate geometry, including the classification of numbers, multi-step equations, and the commutative property. Learn how to locate and graph points using ordered pairs, recognize the components of the coordinate plane, and understand quadrants. This lesson also covers inequalities, proportions, and absolute values, providing a comprehensive overview of analytic geometry and its applications in navigation and mapping. Delve into the contributions of René Descartes and discover how to create and interpret various representations of relations. ###

### Understanding Coordinate Geometry: Key Concepts and Applications ###
E N D
Presentation Transcript
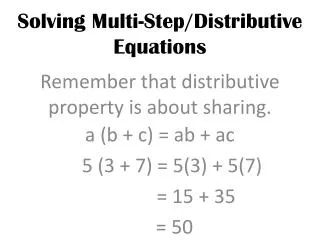
Let’s Review • Commutative Property • Classify Numbers • Multi-Step Equations • Absolute Value • Proportions/Percent of increase/decrease • Inequalities : When to switch sign? • ONE DIMENSION • B.A.G.
“I can…” • …locate and graph points on the coordinate plane and identify the components of a coordinate plane • M(F&A)-10-2 • M(G&M)10-9
Rene Descartes • French mathematician and philosopher • Born 1596 • Law degree in 1616, served in the military for 9 years • Set the stage for ‘Analytic Geometry’ • Also introduced exponents
The Coordinate Plane • To locate a point on a coordinate plane, we use ORDERED PAIRS • The first entry is the X-Coordinate • The second entry is the y-Coordinate
Coordinate Plane • Graph a point- means to draw a dot at the point on the coordinate plane that corresponds to the ordered pair • The coordinate plane is divided into four quadrants
Relations- Think of Languages • A Relation is a set of ordered pairs, a table, a graph, or a mapping • Relations can be represented the following ways…
Relations- Think of Languages • Domain- the x-value of a relation • Range- the y-value of a relation
Example • Create a mapping diagram, table, and a graph of the following data; • (-1,7) (3,1) (-8,-5) (6,13) (7,7) (-8,2)
Inverse • The ‘inverse’ is obtained by switching the x-value and the y-value • Example • (5, -1) (7,2) (-3, -5) (4,8)
Home Work Assignment • Section 4.1/4.3 handout - ALL