Investigating Sealing Challenges in Commercial RF Connectors: A Comprehensive Study
70 likes | 176 Vues
This report details the sealing type experiments conducted at MKS 3, focusing on RF connector CF 16 with diamond shape gaskets. Key findings reveal significant leakage issues influenced by varying tolerances among suppliers and gasket materials. Our investigations uncovered that gaps, hardness discrepancies, and compression forces play critical roles in leak rates. This is the first part of a two-part series highlighting the observed problems with both copper and aluminum gaskets and their effects under varying conditions.

Investigating Sealing Challenges in Commercial RF Connectors: A Comprehensive Study
E N D
Presentation Transcript
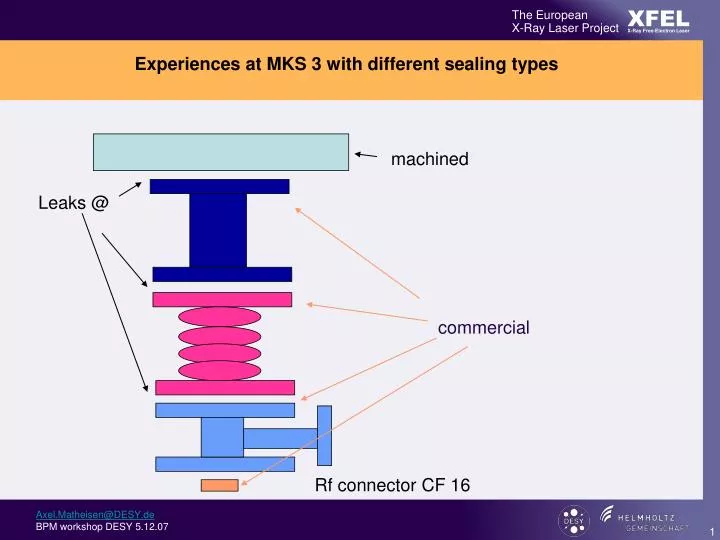
Experiences at MKS 3 with different sealing types machined Leaks @ commercial Rf connector CF 16
Diamond shape gasket Specialty Large gap for rinsing and degreasing ; large “leak seeking” grooves for flushing Guiding “nose”
Problems we found Part 1 Problems observed CF CF system - Tolerances - Supplier of commercial systems have different tolerances from supplier to supplier - „Hand made“ beam pipe to Cf 35 vary in tolerances - Tolerances in Cu gasket (up to 30 % leak rate on some „batches“ observed - Hardness of Cu Al system - Tolerances in height not relevant for Tightness - Actually hardness loose tolerances HB>60 distance flange to flange varies Diameter - Angle of knife edge compression distance flange to flange varies
Forces on gasket Soft Seals
Problems we found part 2 CU Conflat - „0 to 0“ distance leaking - Large gap flange to flange ( Groove not deep enough) leak under non axial forces - Gasket to thin leaking - Gasket OD to small needs to be re tightened down to 0 to 0 distance - CU too soft needs retightening (CF soft CU floating under compression) - Big stainless flange fast T variation leaking • ALMg SI 05 • - Distance 0-0 leaking • Large gap ok • Material too hard No floating no spring loading • (compression forces always at the limit plastic to elastic deformation spring loading effect) • - Gasket OD too small limited leak tightness during T variation • -Material too soft • no defined distance • limited leak tightness due to larger surface( reduced forces on sealing surface) • Harder material • high forces no spring loading effect leaking during cool down