Nervous System III
200 likes | 418 Vues
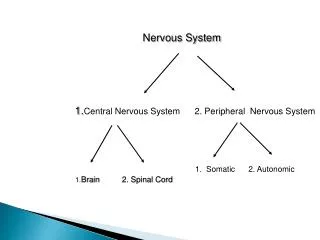
Everybody's got one?. Brain structuresCerebrum (cortex, medulla)CerebellumDiencephalonBrain StemFissures, gyri, sulci. Cerebrum. Cortical lobesmotor areassensory areasassociation areasMedullacerebral nucleitracts. Diencephalon. ThalamusHypothalamusEpithalamus. Brainstem. MidbrainPonsMedulla Oblongata.

Nervous System III
E N D
Presentation Transcript
1. Nervous System III May 3, 2007
BIOL 203
Karen Kraus
2. Everybody�s got one� Brain structures
Cerebrum (cortex, medulla)
Cerebellum
Diencephalon
Brain Stem
Fissures, gyri, sulci
3. Cerebrum Cortical lobes
motor areas
sensory areas
association areas
Medulla
cerebral nuclei
tracts
4. Diencephalon Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Epithalamus
5. Brainstem Midbrain
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
6. The Little Brain Vermis
Arbor vitae
Peduncles
7. Functional Systems Limbic system
hypothalamus
hippocampus
rhinencepalon
prefrontal cortex
fornix
Reticular Activating System
corona radiata
8. Protection racket Meninges
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
Cerebrospinal fluid
Ventricles
Choroid plexus
9. Don�t you have a backbone? C1 through L1
anchored
filum terminale
denticulate ligaments
Enlargements
cervical
lumbar
10. Spinal Cord Cross Section
11. Spinal Tracts Ascending
spinothalamic
spinocerebellar
Descending
corticospinal
12. Good reflexes! Reflex arc
types of reflexes
spinal vs. cranial
innate vs. acquired
somatic vs. autonomic
flexor (withdrawal)
crossed extensor
stretch
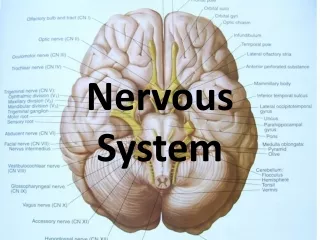
13. The nerve! Facial
Vestibulocochlear
Glossopharyngeal
Vagus
Accessory
Hypoglossal Olfactory
Optic
Oculomotor
Trochlear
Trigeminal
Abducens
14. Spinal nerves 31 pairs
8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccygeal
roots form nerves, which split to form rami
ventral rami from cervical, lumbar and sacral form plexuses
15. Plexus nexus Cervical
phrenic
Brachial
median, radial, ulnar
Lumbar
femoral
Sacral
sciatic, peroneal, tibial
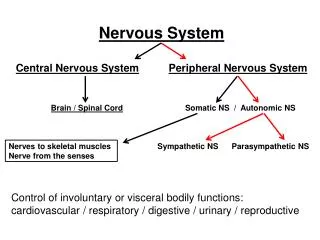
16. Versus Somatic vs. Autonomic nervous systems
functional differences
structural differences
dual innervation
two-neuron chain
myelination
effectors
neurotransmitters
17. Repeat Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic
18. Sympathetic Division
19. Parasympathetic Division
20. Reception Cholinergic
Nicotinic
Muscarinic
Adrenergic
Alpha
Beta
21. Action! Effects of the ANS
sympathetic
generally �fight or flight�
parasympathetic
generally �resting and digesting�