Peripheral Nervous System
170 likes | 445 Vues
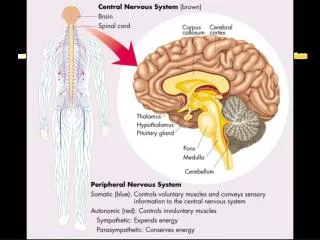
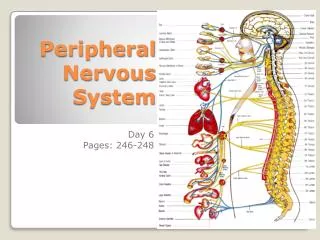
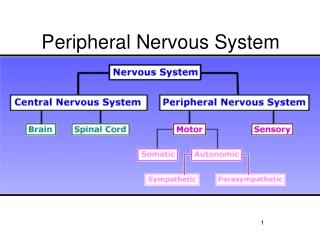
Peripheral Nervous System. Principles of Health Science 2012. Peripheral nervous system is made of all of the nerves . PNS consists of cranial nerves and spinal nerves. Cranial Nerves. 12 pairs and their branches Originate in the brain.

Peripheral Nervous System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Peripheral Nervous System Principles of Health Science 2012
Peripheral nervous system is made of all of the nerves. • PNS consists of cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
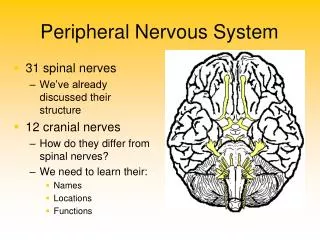
Cranial Nerves • 12 pairs and their branches • Originate in the brain
Some are responsible for special senses such as sight, hearing, taste, and smell.
Some receive general sensations such as touch, pressure, pain, and temperature, and send out impulses for involuntary and voluntary muscle control
Spinal Nerves • 31 pairs and their branches • Carry messages to and from the spinal cord • Both sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) nerves
Consists of the following pairs: • 8 cervical • 12 thoracic • 5 lumbar • 5 sacral • 1 coccygeal
Each nerve goes directly to a particular part of the body or networks with other spinal nerves to form a plexus that supplies sensation to a larger segment of the body.
Autonomic Nervous System • Important part of the peripheral nervous system • Helps maintain a balance in the involuntary functions of the body BUT also allows the body to react in times of emergency
There are two divisions of the ANS: Sympathetic Parasympathetic
Sympathetic and parasympathetic work together • Functions include: • 1. Maintaina balanced state (homeostasis) • 2. Control involuntary body functions at proper rates
SympatheticNervousSystem • Acts in times of emergency: fight or flight • Prepares body to act • Increases heart rate and respirations • Raises blood pressure • Slows activity in digestive tract
Parasympathetic Nervous System • Counteracts actions of sympathetic after the emergency • Slows heart rate and respirations • Lowers blood pressure • Increases activity in digestive tract