Jeopardy
260 likes | 506 Vues
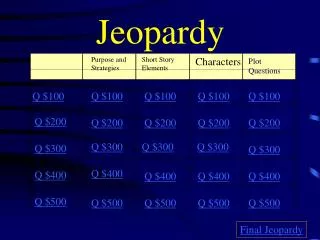
Jeopardy. Name the three types of chromosomes . Sex Chromosomes Autosomal Chromosomes Homologous Chromosomes. Chromosomes for 100 . Back. Chromosomes for 200 . How many chromosomes are in the body cells of a dog that has a haploid number of 39? . 78 chromosomes. Back.

Jeopardy
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Name the three types of chromosomes Sex Chromosomes Autosomal Chromosomes Homologous Chromosomes Chromosomes for 100 Back
Chromosomes for 200 • How many chromosomes are in the body cells of a dog that has a haploid number of 39? • 78 chromosomes Back
Homologous chromosomes contain many genes that code for what type of traits? Same Traits Chromosomes for 300 Back
DNA is compacted by wrapping tightly around proteins. Chromosomes for 400 • In one cell DNA is about 2.5m in length. How can the DNA fit inside a cell that can only be seen with a microscope? Back
Why is DNA only seen during the stages mitosis and not during interphase? DNA is in a uncondensed form (chromatin) during interphase and a condensed form during mitosis. Chromosomes for 500 Back
In what phase does the cell spend majority of its time in? Interphase Mitosis for 100 Back
Identify and describe the stage depicted below: Centromeres double Spindle Fibers shorten chromosomes move to opposite sides of the cell Mitosis for 200 Back
These “cables” extend from the poles during metaphase. What are these cables called? Spindle Fibers Mitosis for 300 Back
What is the end product of mitosis? (be specific) 2 diploid daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell Mitosis for 400 Back
During cytokinesis what forms in a plant cell and an animal cell? Plant Cell – Cell Plate Animal Cell - Furrow Mitosis for 500 Back
In a human cell how many chromosomes are located in the nucleus at the beginning of meiosis? At the end of meiosis? Beginning – 46 End - 23 Meiosis 100 Back
Meiosis for 200 • Identify the following diagrams: • A – Anaphase I • B – Metaphase I A B Back
Name the processes of which sperm and eggs are produced in organisms. Spermatogenesis (male) Oogenesis (female) Meiosis for 300 Back
Meiosis for 400 • What are three ways that cell division lends to genetic variation in a population? • Random fertilization • Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes • Crossing over Back
What stage in meiosis do homologous chromosomes line up together? Why must they line up together? Metaphase I The line up together so the division will produce haploid cells. Meiosis for 500 Back
How do microorganisms produce dairy products? Through fermentation Cellular Respiration for 100 Back
What is the order of stages for aerobic respiration? Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain Cellular Respiration for 200 Back
During the electron transport chain, electrons lose energy creating ______ to create an electrical gradient that produces ATP. Protons Cellular Respiration for 300 Back
When are muscles are fatigued they tend to become cramped. Describe what is happening in terms of cellular respiration. The muscle cells are switching to anaerobic respiration due to the lack of oxygen. The muscles are going through fermentation. Cellular Respiration for 400 Back
How much ATP is created by the breakdown of one glucose molecule in glycolysis? And how much is made during the entire aerobic respiration? 2 ATP 38 ATP Cellular Respiration for 500 Back
What does it mean when the cell membrane if referred to as selectively permeable? only certain particles can pass through Cell Transportation for 100 Back
What kind of particle crosses the lipid bilayer most easily? water Cell Transportation for 200 Back
Some animal cells protect themselves from absorbing too much water by “pumping” excess water out. They use a __________ to do this. Contractile Vacuole Cell Transportation for 300 Back
When the concentration of solutes inside a the cell is equal to the concentration of solutes outside the cell, the solution is said to be … Isotonic Cell Transportation for 400 Back
What process helps the cell rid itself of wastes. Exocytosis Cell Transportation for 500 Back