Momentum and Impulse Theorem
40 likes | 131 Vues
Explore the concept of momentum as "mass in motion" and how it relates to objects in motion. Learn about examples like airbags in automobiles and Newton's cradle, illustrating the principles of momentum. Discover the connection between force, impulse, and changes in momentum.

Momentum and Impulse Theorem
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Momentum and Impulse Theorem By CorinaBot
Definition: Momentum can be defined as "mass in motion." All objects have mass if an object is moving, then it has momentum it has its mass in motion. • Examples: • air bags in automobiles. Air bags are used in automobiles because they are able to minimize the affect of the force on an object involved in a collision. Air bags accomplish this by extending the timerequired to stop the momentum of the driver and passenger. • Newton’s cradle http://femto.cs.uiuc.edu/~sbond/reports/MATH_996/newtonscradle-animation.gif http://www.physicsclassroom.com
A car is traveling at a velocity of 20 m/s on a straight road. Mass of the car is 1300 kg. A motorcycle passes the car at a speed of 40 m/s. The motorcycle with its rider has a mass of 370kg. Which one has a higher momentum? Why ? For the car: For the motorcycle and rider: The car has more momentum than the motorcycle even though its velocity is half.
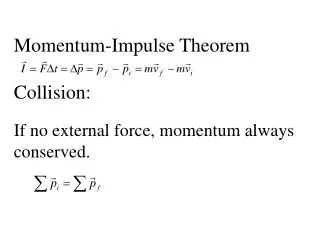
When a force is applied to a rigid body it changes the momentum of that body. Impulse = Change in momentum Momentum examples video www.sciencemuseum.org.uk http://www.salk.edu/