Capsule Endoscopy
300 likes | 1.04k Vues
Capsule Endoscopy. Barbara Bisseker Inflammatory Bowel Disease Nurse Specialist George Eliot Hospital, Nuneaton. Video. How did Capsule Endoscopy originate?. Developed by Gavriel Iddan an electro-optical engineer who worked for the Israeli defence agency

Capsule Endoscopy
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Capsule Endoscopy Barbara Bisseker Inflammatory Bowel Disease Nurse Specialist George Eliot Hospital, Nuneaton
How did Capsule Endoscopy originate? • Developed by Gavriel Iddan an electro-optical engineer who worked for the Israeli defence agency • Neighbour (a gastroenterologist) who told him about conventional endoscopy • 20 years of development the first capsule was showcased at the 11th world congress on Gastroenterology in Vienna 1998 • Within 3 years it was given approval by USA food & Drug Administration
What is Capsule Endoscopy? • Non-invasive, patient friendly, ambulatory and cost effective procedure designed to visualise the entire small bowel, oesophagus and colon. • The capsule is a small, pill-size capsule that is swallowed by the patient with a sip of water and following a period of NBM. • 2 frames per second delivers approx 83,000 images. It is propelled through the gut by peristalsis
Capsule Endoscopy • December 2004 NICE issued guidelines for use – mainly for the cause of OGI bleeding in the presence of a normal OGD & Colonoscopy • 2008 BSG guidelines on Small bowel enteroscopy and capsule endoscopy in adults
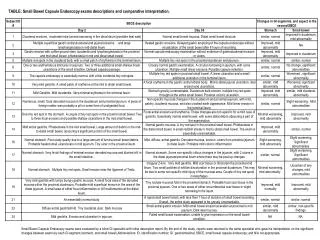
Capsule Endoscopy - Clinical efficacy • Meta-analysis of 14 studies reported yields 63% for CE compared with 28% for PE Triester et alAmerican Journal of Gastroenterolgy 2005 • Yield of CE superior to barium follow through and CT enteroclysis Nakamura et al Endoscopy 2006 • Further meta-analysis of 17 studies shows CE superior to all other modalities. Rate of positive finding in CE 95% compared with 44% Marmo et al. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2005
Capsule Endoscopy • Patients with OGI bleeding with a –ve OGD & colonoscopy should undergo capsule endoscopy • If there is a high suspicion of bleeding from UGI source, a second look OGD should be performed prior to CE • All patients should be counselled on the risks of capsule retention • Those with pathology/bleeding identified on CE should undergo PE or DBE • Therapy to minimise further bleeding • In patients with a –ve CE & persistent OGB, a second CE could be considered • CE should be considered for patients with a high suspeicion of small bowels Crohn’s disease where other investigations are –ve. • CE for patients with refactory Coeliac disease to look for complications.
Diseases; Crohn’s Disease Familial Adenomatous Polyposis Peutz Jaegers Disease Polyposis Small Bowel Tumours OGIB Coeliac Disease Tumours Iron Deficiency Anaemia Contraindications: Known or suspected strictures (Patency Capsule) Swallowing Disorders (AdvanCE) Zenkers Diverticulum Pregnancy Pacemakers (not any more?) Disease indications and contraindications
Capsule Endoscopy – Information for patients • Stop iron preparations at least 7 days prior to procedure • Avoidance of codeine based medications • Liquid diet from lunchtime the day before & NBM from 10pm • Men – shave abdomen (not necessary if using ‘Sensorbelt’) • Warning that the patient may present a worrying appearance to general public
Capsule Endoscopy – Day of Procedure • Short interview to ensure no contra-indications • Explanation to the patient about what is to happen. • Sign consent form – risks/benefits
Capsule Endoscopy A short demonstration Can I have a volunteer?
Capsule Endoscopy • Attach Sensor array or Sensorbelt • Swallow capsule with small sip of water & simethicone • Patient asked to lie on their right side • Connect up to ‘Realtime viewer’ • Once happy capsule is in the SB, patient can go home • Telephone contact number should there be problems
Capsule Endoscopy - Complications • Main risk is retention 0.75% (capsule remaining in the digestive tract for more than 2 weeks or more requiring directed medical, surgical or endosopic intervention). BSG Guidelines 2008 • Patients must not undergo MRI until they have passed the capsule
Capsule Endoscopy • Return equipment the following day either in person or by post • Data from recorder is downloaded onto a computer workstation • Approx 50,000 images can be reviewed as a video • Reading time 40-60mins dependent upon experience of reader.
PillCam ESO Oesophageal Capsule Images Normal Z-Line Suspected Barrett’s Esophagitis Varices
PillCam Colon Images Diverticulosis Large Neoplastic Tumor Ulcerative Colitis Sessile Polyp Pedunculated Polyp Pedunculated Polyp
Capsule Endoscopy - Training • ‘On the job’ training • Courses provided by manufacturing company • On-line module – Wolfson Unit
Capsule endoscopy Thank you – any questions?