Polynomial Functions
110 likes | 368 Vues
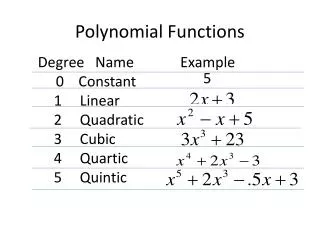
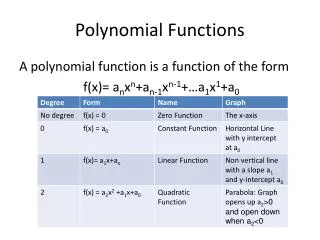
Polynomial Functions. Lesson 9.2. Polynomials. Definition: The sum of one or more power function Each power is a non negative integer. Polynomials. General formula a 0 , a 1 , … ,a n are constant coefficients n is the degree of the polynomial

Polynomial Functions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Polynomial Functions Lesson 9.2
Polynomials • Definition: • The sum of one or more power function • Each power is a non negative integer
Polynomials • General formula • a0, a1, … ,an are constant coefficients • n is the degree of the polynomial • Standard form is for descending powers of x • anxn is said to be the “leading term”
Polynomial Properties • Consider what happens when x gets very large negative or positive • Called “end behavior” • Also “long-run” behavior • Basically the leading term anxn takes over • Comparef(x) = x3 with g(x) = x3 + x2 • Look at tables • Use standard zoom, then zoom out
Polynomial Properties • Compare tables for low, high values
The leading term x3 takes over For 0 < x < 500the graphs are essentially the same Polynomial Properties • Compare graphs ( -10 < x < 10)
Zeros of Polynomials • We seek values of x for which p(x) = 0 • Consider • What is the end behavior? • What is q(0) = ? • How does this tell us that we can expect at least two roots?
Methods for Finding Zeros • Graph and ask for x-axis intercepts • Use solve(y1(x)=0,x) • Use zeros(y1(x)) • When complex roots exist, use cSolve() or cZeros()
Practice • Giveny = (x + 4)(2x – 3)(5 – x) • What is the degree? • How many terms does it have? • What is the long run behavior? • f(x) = x3 +x + 1 is invertible (has an inverse) • How can you tell? • Find f(0.5) and f -1(0.5)
Assignment • Lesson 9.2 • Page 400 • Exercises 1 – 29 odd