Nervous System- Divisions
190 likes | 909 Vues
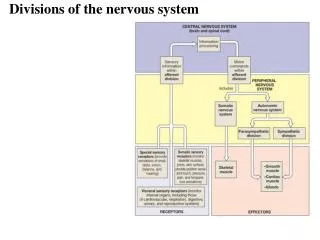
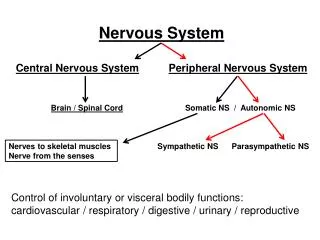
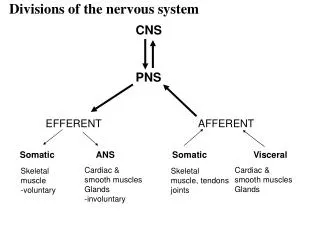
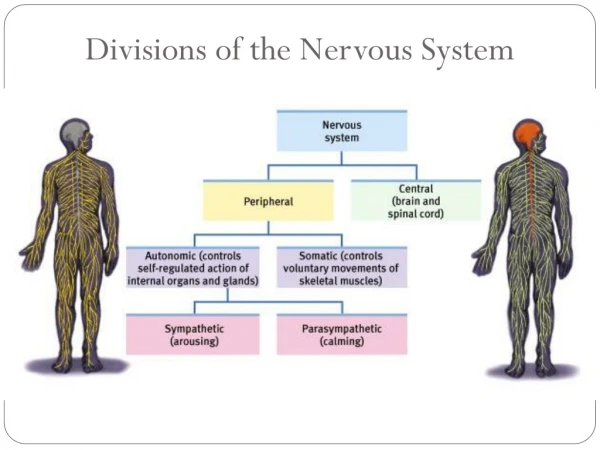
Nervous System- Divisions. Central Nervous System (CNS) - brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) - nerves extending to extremities Autonomic nervous system (ANS) - regulates body’s automatic or involuntary functions. Nervous System: Cells. Neurons: Structure Cell Body

Nervous System- Divisions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Nervous System- Divisions • Central Nervous System (CNS) - brain and spinal cord • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) - nerves extending to extremities • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) - regulates body’s automatic or involuntary functions
Nervous System: Cells • Neurons: Structure • Cell Body • Dendrites • Axon • myelin - • Schwann cells - • myelinated fibers - • nodes of ranvier -
Nervous System: Cells • Neurons - 3 Types • Sensory neurons • Motor neurons • Interneurons • Glia - connective tissue cells of the CNS • Astrocytes - star shape (attach to blood vessels) • Microglia - consume microbes • Oligodendroglia - produce myelin sheath
Nervous System: Tissue Disorders • Multiple sclerosis: myelin disorder • Tumors: neuroma • Multiple neurofibromatosis: inherited fibrous neuromas
Nervous System: Nerves • Nerve - bundle of peripheral axons • Tract - bundle of central axons • White matter - myelinated axons • Gray matter - unmyelinated axons • Nerve coverings - fibrous connective tissue • Endoneurium- surrounds single fiber • Perineurium- surrounds group of fibers • Epineurium- surrounds entire nerve
Nervous System: Reflex Arcs • Reflex Arc - Nerve impulses traveling to and from the brain. • Receptors - beginning of dendrites • Ganglion - nerve cell bodies in PNS • Synapse - space between axon and dendrite • Reflex - response to impulse over a reflex arc • See pg. 205
Nervous System: Nerve Impulses • wave of electrical disturbance that travels along the surface of a neuron’s plasma membrane • impulse created by an imbalance of sodium ions on the inside and outside of the plasma membrane • saltatory conduction - fast impulse on myelinated plasma membrane
Nervous System: Synapse • Synapse- impulse passed from one neuron to the next • Neurotransmitters - chemical compounds released from axon terminals into a synaptic cleft (pg. 208) • acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, catecholamines, endorphins, enkephalins
Nervous System: Parkinson’s Disease • chronic nervous disorder resulting from a deficiency of dopamine
Central Nervous System • Divisions of the Brain: • Brain Stem • Medulla Oblongata • Pons • Midbrain • Cerebellum • Diencephalon • Hypothalamus • Thalamus • Cerebrum
CNS: Brain Stem • medulla oblongata - enlarged upper section of the spinal cord • pons - above medulla oblongata • midbrain- rests between the pons, thalamus, and cerebellum • all three contain well mixed white and gray matter • function: two-way conduction paths
CNS: Diencephalon • lies between the brain stem and cerebrum • Hypothalamus - consists mainly of the posterior pituitary gland, pituitary stalk, and gray matter • Functions: Center for controlling ANS, controls hormone secretion, and controls appetite, wakefulness, and pleasure
CNS: Diencephalon cont... • Thalamus: dumb-bell shaped mass in each cerebral hemisphere • Relays sensory impulses to cerebral cortex • Produces the emotions of pleasantness and unpleasantness associated with sensations
CNS: Cerebellum • Lies below occipital lobe • Outer layer - gray matter • Inside - White matter • Functions - Produce smooth coordinated movements • Maintain equilibrium • Sustain normal postures
CNS: Cerebrum • Largest part of brain • Outer layer - gray matter (cerebral cortex) • Interior of brain - white matter (tracts) • two lobes • Functions - mental processes of all types (sensations, consciousness, memory, and voluntary control of movements)
Peripheral Nervous System • Cranial Nerves (12 Pair) • Spinal nerves • Peripheral nerve disorders • Neuritis • Trigeminal neuralgia • Bell’s palsy • Shingles
Autonomic Nervous System • Regulates the body’s automatic or involuntary movements (main job is to restore homeostasis) • Sympathetic Vs. Parasympathetic • Autonomic Neurotransmitters • Disorders of ANS • Stress induced disease • Neuroblastoma