DOL level 4 week11
280 likes | 423 Vues
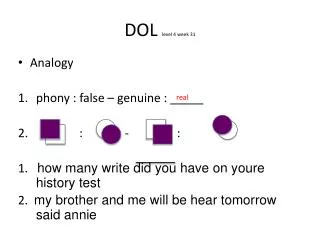
DOL level 4 week11. Analogy Saturday: ________ - Thursday : Thurs. baseball : diamond – tennis : ________ 1. which of the three boys is older 2. beth has chose mary jane to be her partner on the trip too indianapolis. Sat. court. Pledge. Fluency. 6 min. reading solution.

DOL level 4 week11
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DOL level 4 week11 • Analogy • Saturday: ________ - Thursday : Thurs. • baseball : diamond – tennis : ________ 1. which of the three boys is older 2. beth has chose mary jane to be her partner on the trip too indianapolis Sat. court
Fluency 6 min. reading solution
Objectives day 1 Students will • Identify synonyms • identify the spelling changes in a root word because of affixes.
Word Structure day 1 Line 1 Line 2 Line 3 Line 4
Word Structure day 1 • The spelling of a base word often changes when an affix is attached to it. • For some prefixes, the way in which the prefix is spelled depends on the letter with which the root word begins. • The words in each pair are synonyms—they are similar in meaning. several and many, true and correct. • Think of other pairs of synonyms. Line 1
Fluency 6 min. reading solution
bitterly branch She bitterly told her sad tale. She wanted to branch out in other hobbies. Vocabulary lesson 3 Harshly, extremely To divide and subdivide depend linked She learned to depend on her friends. We are linked together as humans. To connect (past tense of link) To need; to rely on
microscope seaweed She viewed the bacteria on her microscope She got tangled in the seaweed. Vocabulary lesson 3 Tool for looking at very small things A plant that grows near surface of sea. slightly photosynthesis She was slightly warmer when the sun came out. The process by which green plants combine carbon dioxide, water and sunlight to produce food. By a little bit
Purpose Big Idea What role do you play in natures delicate balance?
Building Background • What have you eaten recently • What articles about food chains have you read recently?
Build Background • Producers are the plants and vegetables at the beginning of the food chain. They make food with the sun’s energy through a process called photosynthesis.
Build Background Consumers are the organisms that eat. There are primary and secondary consumers. Primary consumers, also known as herbivores, eat only plants. These include animals such as cows, squirrels, and deer.
Build Background Secondary consumers, also known as carnivores, eat primary consumers. For example a cat might eat a mouse. Omnivores are consumers that eat plants and animals. Human beings are omnivores.
Who Eats What? pg 170 Set a purpose for reading, such a for personal enjoyment or to learn something.
Objectives Students will Use comprehension Strategies Clarifying Summarizing Visualizing Asking Questions
Reading the Selection Genre Expository Text • Is presented in a straightforward way • can be organized by topics • can include diagrams, photographs, maps, or illustrations to help the reader understand the subject better • can be checked by other sources.
Comprehension Strategies Clarifying summarizing visualizing asking questions
Handing Off Have you grasped the following ideas? Why certain animals are at the top of food chain Why all animals depend on green plants for food What happens when one of the links in a food chain is removed?
Inquiry ProcessWhole-Group Time • Make a Conjecture A conjecture is a kind of theory, an explanation of something that we suggest before we have a great deal of evidence. Conjectures can be proved to be right or wrong, or they can be modified in some way by the evidence. Example: How does gravity affect energy in things that are not alive? I am not sure, but I think that what causes a rock to roll down a hill is not just that someone has pushed it. Gravity also pulls the rock down the hill. /But if the rock is heavy, it might not be pulled as fast a lighter rock. The first pat of the conjecture is accurate, but the second part is not. Record your conjecture on a paper and post it on the Concept/Question Board.
Writing an Informative Report An informative report is where students answer questions about something they are interested in by gathering information and presenting it Caution: Be careful not to choose a topic that is too big. Narrow your topic to one you can cover in the assigned length of time. Be careful about organization. Decide on your topics, subtopics, and details you want to include.
GrammarSentences with compound subjects Skills Practice 1 pages 101-102 Hawks eat chipmunks. Weasels eat chipmunks. • A simple sentence has a subject and a predicate. The subject and predicate may be simple or compound. • A compound subject has two or more subjects and the same predicate. Hawks and weasels eat chipmunks. • Compound subjects are usually linked by the conjunction and, Hawks and weasels comprise the compound subject. They share the simple predicate eat chipmunks. • Write a couple of compound sentences and exchange the sentences with a partner. Identify the subjects.