The Neolithic Revolution (?)
820 likes | 1.07k Vues
The Neolithic Revolution (?). Books to read. Robert J. Wenke. Patterns in Prehistory: Humankind’s First Three Million Years Charles Keith Maisels. The Emergence of Civilization: From Hunting and Gathering to Agriculture, Cities, and the State in the Near East

The Neolithic Revolution (?)
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Books to read • Robert J. Wenke. Patterns in Prehistory: Humankind’s First Three Million Years • Charles Keith Maisels. The Emergence of Civilization: From Hunting and Gathering to Agriculture, Cities, and the State in the Near East • The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena and Prehistory
Origins of Agriculture • humans as hunters and gatherers • Until • dominated by the environment • constant movement the norm
Two points extra on the first test for the person who can tell me within 3 years when this painting was made.
Living area ? • tropical areas: one sq.. mile per person • colder climates: 20-30 sq. miles per person • for 30 people: almost 1000 sq. miles • life is “nasty, brutish, and short”
Radical Change • the Neolithic Age (New Stone Age) • radical change in the acquisition of food • humans began to consciously produce food
Neolithic differences • grinding stone tools • more durable than flint or chert • obtained food wholly or primarily by organized agriculture and/or animal husbandry • rather than hunting and gathering
Flaked stone Polished stone
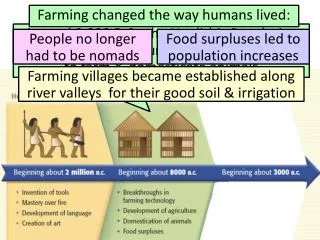
Most important change • organized agriculture • sedentary life-style • based on farming a few simple crops • for surplus
When and Where? • Middle East • about 10,000 B.C. • near the end of the last ice age
How did it happen? • some single genius? • accident? • in human history: never underestimate stupidity and accident • the genius is the one who figures out how to really screw up productively
What did humans know? • empirically aware of the natural cycle of plants? • plants come from seeds? • they need water and sunlight? • same time, same place, each year?
Why did it take so long? • traditional explanation: no incentive • hunter and gatherers maintain small populations • infanticide, abortion, lactation taboos • lacking stimulus for radical change?
Problems and Advantages • food supply is at the mercy of the elements • food supply is more varied and healthy • food supply requires less work to acquire • nomadic lifestyle avoids disease
Why the Shift? • end of the Ice Age: climate and environment change? • population growth
Alternative theories • accident • accident and stupidity • accident and good luck
Other reasons for slow change? • number of plants suitable for domestication • 3,000 of 200,000 plants are suitable • depending on climate and local • only 30 (or so) are of major importance
Domestic plants? (sedentary agriculture) • four grasses: wheat, maize, rice, sugar • starches: potatoes, yam, manioc, banana • legumes: lentils, peas. wetches, beans, peanuts, soybeans
Domestic animals? (pastoralism) • not many • and how exactly do you domesticate them, anyway?
So why did people change? • why leave a relatively casual hunting-and-gathering life • for the seven-days-a-week life of a farmer • forced to do so by climatic change? • forced to do so by gradual (over the centuries) population growth ? • accidental by-product of trade ?
Advantages ? • support more people per sq. mile • security
Change • between 10,000 and 2,000 years ago • most humans switched to organized agriculture • in whole or in part
Location: early origins • Asia Minor • Palestine • Iranian Plateau
Surplus Food and the Specialization of Labor • Emergence of villages and towns • Discoveries at Çatal Hüyük, Turkey, occupied 7250-5400 BCE • Tremendous range of manufactured products • Pottery, Jewelry, Textiles, Copper tools • Development of crafts
Catal Huyuk: Their view