EXCRETORY SYSTEM
260 likes | 555 Vues
EXCRETORY SYSTEM. WHAT IS THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM?. System in the body that collects wastes produced by cells and removes the wastes from the body. WHAT DOES THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM REMOVE?. UREA Poisonous chemical that comes from the breakdown of proteins WATER. EXCRETORY ORGANS. KIDNEYS.

EXCRETORY SYSTEM
E N D
Presentation Transcript
WHAT IS THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM? • System in the body that collects wastes produced by cells and removes the wastes from the body.
WHAT DOES THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM REMOVE? • UREA • Poisonous chemical that comes from the breakdown of proteins • WATER
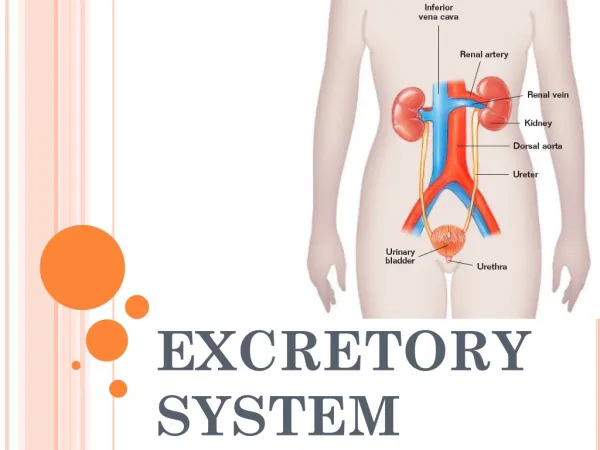
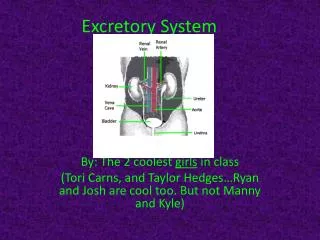
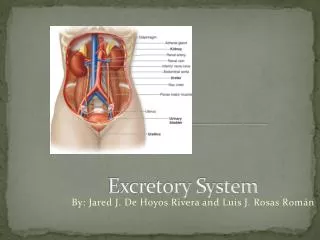
KIDNEYS • Act as filters • Blood flows through kidneys, wastes are removed from the blood • One drop of blood will pass through the kidneys 300 times a day • Each kidney contains about 1 million filtering factories called nephrons.
NEPHRONS • Filtering factories in kidneys • Removes wastes from blood (urea,water), sends needed materials (glucose, water) back to blood
URINE • Nephrons form a liquid wasted called URINE. • Made up of urea, water, and other wastes. • Bright Yellow Lots of urea • Clear Lots of water
URETER • Urine exits the kidneys and travels through the URETER. • Narrow tubes that connect to the bladder.
BLADDER • A saclike muscular organ that stores urine. • When the bladder is full enough, that is the walls are stretched, you feel a need to urinate. • Bladder hold approx. 2 cups of urine.
URETHRA • Small tube connects bladder to the outside of body. • Muscle at the end of the urethra contracts and relaxes to remove urine.
DIALYSIS • People who do not have functioning kidneys undergo dialysis. • Blood is removed from body, is filtered through a machine which cleans the blood. • It removes wastes and puts needed materials back into the blood. • The blood then enters the body again.
KIDNEY STONE • A kidney stone is a solid mass of tiny crystals trapped in the kidney or ureter. • Block urine from passing to bladder. • Cause swelling and pain in kidneys. • Can “pass” if small, may need to be surgically removed in too large.
URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) • Infection that can happen anywhere along the urinary tract. • Caused by germs, usually bacteria that enter the urethra and then the bladder. This can lead to infection, most commonly in the bladder itself, which can spread to the kidneys.