Chapter 17 Amines ( 胺 )
500 likes | 1.15k Vues
Chapter 17 Amines ( 胺 ). 17.1 Amine Nomenclature 17.2 Structures of amines 17.3 Basicity of amines 17.4 Preparation of amines 17.4.1 Preparation of amines by alkylation of ammonia 17.4.2 The Gabriel synthesis of primary amines

Chapter 17 Amines ( 胺 )
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 17 Amines (胺) 17.1 Amine Nomenclature 17.2 Structures of amines 17.3 Basicity of amines 17.4 Preparation of amines 17.4.1 Preparation of amines by alkylation of ammonia 17.4.2 The Gabriel synthesis of primary amines 17.4.3 Preparation of amines by reduction 17.5 Reactions of amines 17.5.1 Alkylation of amines 17.5.2 Acylation of amines 17.5.3 The Hofmann Elimination
17.5.4 Reactions of amines with nitrous acid (A) Reactions of primary aliphatic amines with nitrous acid (B) Reactions of primary arylamines with nitrous acid (C) Reactions of secondary amines with nitrous acid (D) Reactions of tertiary amines with nitrous acid 17.5.5 Synthetic transformations of aryl diazonium salt (A) Replacement of the diazonium group by -OH
(B) Replacement of the diazonium group by -X, -CN (c) Replacement of the diazonium group by -H 17.5.6 Azo coupling 17.6 Spectroscopic analysis of amines
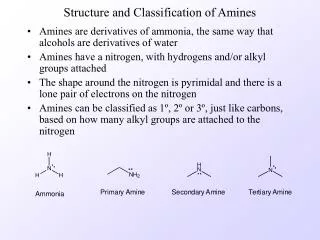
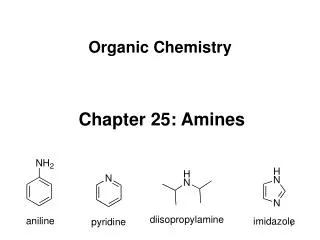
17.1 Amine Nomenclature P380 Organic derivatives of ammonia Alkylamines Arylamines Primary amines(伯胺): Aniline (苯胺) Methylamine (甲胺) Isobutylamine (异丁胺) 2-Methylpropylamine (2-甲基丙胺) Benzylamine (苄胺)
Cyclohexylamine (环己胺) Secondary amines: (仲胺) Ethylmethylamine (甲乙胺) N-Methylethylamine (N-甲基乙胺) Diethylamine (二乙胺) Tertiary amines: (叔胺) Trimethylamine N,N-Dimethylmethylamine (三甲胺) (N,N-二甲基甲胺) N,N-Dimethyl- aniline (N,N-二甲基苯胺)
N-Ethyl-N-methylcyclohexylamine (N-甲基-N-乙基环己胺) Diamines: 1,2-Ethyldiamine (1,2-乙二胺) Ammonium ions (铵离子) Aminium salts (铵盐) Anilinium chloride (盐酸苯胺) Quaternary ammonium salts (季铵盐) 2-Aminoethanol (2-氨基乙醇)
Pyridine (吡啶) Pyrrole (吡咯) Quinoline (喹啉) Indole (吲哚) Pyrrolidine (吡咯烷) (四氢吡咯) Piperidine ( 哌啶) Heterocyclic amine: (杂环胺)
sp3-sp3 hybridized orbitals overlap C-N: sp3hybridized -1s orbitals overlap N-H: 17.2 Structures of amines P383, 12.2 N: 1s22s22px12py12pz1 sp3-hybrid Pyramid(棱锥型) Tertiary amines with 3 different groups: Interconversion of amine enantiomers
Quarternary ammonium salt: 17.3 Basicity of amines P384, 12.3 Weak bases
pKb Amines 4.7 3.4 3.3 4.3 9.4 13 8.7 NH3 CH3NH2 (CH3)2NH (CH3)3N Table 1 Basic strength of some amines P385, Table 12.1
2. 1. All amines are weak bases: H2O < RNH2 < < OH- P384, 12.3 Alkylamines are slightly stronger bases than ammonia; Arylamines are much weaker bases than ammonia and alkylamines. p -πconjugation +I Delocalization of nitrogen lone-pair electrons Decreasing the electron density at nitrogen.
pKa = -logKa pKa + pKb = 14 Weaker base:Smaller pKa for ammonium ion Stronger base: Larger pKa for ammonium ion
3. R2NH > RNH2 > R3N >NH3 Poorer solvation Anilinium ion Separation of amines from neutral organic compounds P384, 12.3 17.4 Preparation of amines 17.4.1 Preparation of amines by alkylation of ammonia
17.4.2 The Gabriel synthesis of primary amines Primary alkyl halide, SN2 Potassium salt of Phthalimide (邻苯二甲酰胺钾盐) Reagent: Ch.P436 Imide (酰亚胺)
ArX 17.4.3 Preparation of amines by reduction Reduction of nitriles to amines LiAlH4
Siegmund Gabriel was born in Berlin,Germany,and received his Ph.D. in1874 at the University of Berlin, working with August von Hofmann. After further work with Robert Bunsen, he became Professor of Chemistry at the Univ. of Berlin. Robert Wilhelm Bunsen 1811-1899 poohbah.cem.msu.edu/ Portraits/ Siegmund Gabriel (1851-1924)
Gabriel Synthesis. Gabriel, Ber. 20, 2224(1887). M. S. Gibson, R. W. Bradshaw, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 7, 919 (1968); B. Dietrich et al.,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 103, 1282 (1981); O. Mitsunobu, Comp. Org. Syn. 6, 79-85 (1991). Modified conditions: S. E. Sen, S. L. Roach, Synthesis 1994, 756; M. N. Khan, J. Org. Chem. 61, 8063 (1996). Stereoselectivity: A. Kubo et al.,Tetrahedron Letters 37, 4957 (1996).
Reduction of nitro compounds to arylamines P389 H2, cat Reduction of amides to amines:
Reductive amination: Imine (亚胺) Ch.P435
+ H X + 17.5 Reactions of amines Unshared electron pair of nitrogen: Basicity: Nucleophilicity: 17.5.1 Alkylation of amines
(cyclohexylmethyl)- trimethyl- ammonium iodide (99%) (Cyclohexyl- methyl)- amine Methyl iodide 17.5.2 Acylation of amines Acylating agents: acyl chlorides, carboxylic acid anhydrides Synthesis of Paracetamol (扑热息痛):
Hexylamine Hexyltrimethylammonium iodide Decreasing the activity of aryl ring or Protecting amino groups : 17.5.3 The Hofmann Elimination Methylation of an amine by excess CH3I:
Quaternary ammonium hydroxides (氢氧化季铵碱)can be prepared from Quaternary ammonium halides: Quaternary ammonium hydroxides to form alkenes and an amine heat β- Elimination Methylenecyclohexane (亚甲基环己烷) (69%) Ch.P448 (六)
Transition state E2 Reaction Anti relationship The base attacks the most acidic hydrogen or least hinder hydrogen. Regioselectivity of Hofmann elimination: To give a less substituted alkene.
C1–C2 C2–C3 Hofmann rule is opposed to the Zaitsev rule.
August Wilhelm von , 1818–1892, German organic chemist. He was Professor at the Univ. of Berlin from 1865 and was a founder (1868) of the German Chemical Society. He studied the constitu- tion of aniline and was the first to prepare rosaniline and its derivatives, thereby laying the basis for the aniline dye industry. He also discovered a reaction for deriving amines from amides and developed the Hofmann method of finding the vapor densities, and from these the molecular weights, of liquids. He also helped to popularize the concept of valence (the word comes from his term quantivalence August Wilhelm von 1818–1892
17.5.4 Reactions of amines with nitrous acid (Nitrosation亚硝化反应) (A) Reactions of primary aliphatic amines with nitrous acid Nitrosating agent: Primary aliphatic amines Nitrous acid to yield unstable aliphatic diazonium salt (重氮盐) Diazotization (重氮化反应) Aliphatic diazonium salts decompose to form carbocations and nitrogen:
Alkene, alcohol, alkyl halide (B) Reactions of primary arylamines with nitrous acid P390 Primary arylamines form diazonium salt on nitrosation: Aryl diazoniumsalts are stable below 5℃
(C) Reactions of secondary amines with nitrous acid Secondary amines: both aryl amines and alkyl amines react with nitrous acid to yield N-nitrosoamines(亚硝胺) N-nitrosoamines are usually separated from the reaction mixture as oily yellow liquids (D) Reactions of tertiary amines with nitrous acid
Tertiary aryl amines react with nitrous acid to form C-nitroso aromatic compounds: Electrophilic aromatic substitution () 17.5.5 Synthetic transformations of aryl diazonium salt The diazonium group (重氮基)may be replaced by other atomes or groups: -X, -OH, -CN and -H. P391
p-Isopropylaniline p-Isopropylphenol (73%) Aryl diazonium salts can be prepared from arene: (A) Replacement of the diazonium group by -OH Aryl diazonium ion is converted to phenols(酚) Hydrolysis :Electron-withdrawing group Sulfuric acid is usually used instead of hydrochloric acid Question: Design a synsthesis of
(B) Replacement of the diazonium group by -X, -CN The preparation of aryl iodides (81%) The preparation of aryl fluorides: Treating the diazonium salt with fluoboric acid (HBF4) (69%)
The Sandmeyer reaction: Aryl diazonium salts react with cuprous chloride, cuprous bromide, cuprous cyanide (70% overall) (65% overall)
Born inWettingen near Zurich, and lived in the Zurich area for nearly all of his life. He trained as a precision instrument-maker, but became interested in chemistry. Self-educated in chemistry, he carried out chemical experiments in his kitchen. In 1881, he became a lecture assistant to Victor Meyer (1848-1897). He followed Meyer to Göttingen in 1886, but soon returned to Zurich and worked for Arthur Hantzsch (1857-1935). Sandmeyer joined Geigy as a research scientist in 1888, and eventually became a director of the firm. He discovered the decomposition of aryl diazonium Chlorides to chloroarenes in the presence of copper (I) chloride in 1884. He also worked on the triphenylmethane dyes and the synthesis of isatin. Many years before, he had suggested to Victor Meyer an impurity in commerical benzene was responsible for the isatin reaction with sulphuric acid, thereby paving the way for Meyer's discovery of thiophen. Traugott Sandmeyer (1854-1922).
(C) Replacement of the diazonium group by -H Aryl diazonium salts react with hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2) (次磷酸) or ethanol to yield the product: P392 Deamination (脱氨基作用) (85%)
1,3,5-Tribromo- Benzene(74-77%) Aniline 2,4,6-Tribromoaniline (100%) • The value of diazonium salts in synthesis: • Substituents that are otherwise accessible • only with difficulty, such as -F, -I, • -CN, -OH, may be introduced onto • a benzene ring. • Compounds that have substitution patterns • not directly available by electrophilic • aromatic substitution can be prepared
17.5.6 Azo coupling (偶氮偶合反应) Aryl diazonium salts are weak electrophiles, they react with highly reactive aromatic compounds, to yield azo compounds Alkaline solution Azo dyes (偶氮染料) Orange II: P393
17. 6 Spectroscopic analysis of amines Ch.P437(四) IR: 3000-3500 cm-1 two peaks Streching vibration Primary amine 3280 cm-1 one peak Secondary amines Tertiary amines No peak Aliphatic amines Streching vibration 1020-1220 cm-1 Aromatic amines 1250-1360 cm-1
N–H Stretchingvibration C–N Stretching vibration Infrared spectrum of isobutylamine
苯环 伸缩 N-H伸缩 C-N伸缩 N-甲基苯胺的红外光谱
1H NMR N - H δ:0. 6 ~ 5 ppm δ:2.2 ~ 2.8 ppm
Problems to Chapter 17 12.41 12.42 12.48 12.51 12.52 P402 12.21 (a), (d),(e) 12.22 (a), (c),(f) 12.24酶斯卡灵,一种 高效的致幻剂。从 仙人掌中得来。 12.27(b), (d), 12.29(b), (c) 12.30 (a) 12.31(b), (c) 12.37 12.39
Additional Problems to Chapter 17 • What are the major products you would • expect from Hofmann elimination of the • following amines? Show the reactions. 1 • N-Methylcyclopentylamine • (c) 2. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions.Give the major product.
(3) How would you prepare the following compounds from toluene? A diaonio (重氮盐)replacement reaction is needed in some instances. (4) Ch.P464 (十六), (十七)