Understanding Circular Motion and Centripetal Force: Concepts and Calculations
290 likes | 479 Vues
This video explores the principles of circular motion and centripetal force, detailing how angles are measured in radians and relating angular velocity and linear speed. Key equations are presented for calculating centripetal force, along with practical examples, such as a vehicle navigating a curve and analyzing the forces at play. Learn about mass, velocity, radius, and the impact of banked corners and friction coefficients on motion. Suitable for physics students and enthusiasts, this video is an essential guide to mastering circular dynamics.

Understanding Circular Motion and Centripetal Force: Concepts and Calculations
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Circular Motion Centripetal Force
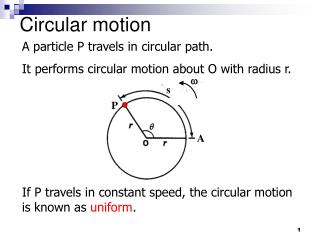
Angles can be measured in RADIANS The angle in radians is s/r which is the length of the arc divided by the radius One full circle = 2𝜋 radians i.e. 360o = 2𝜋 radians
Angular velocity (𝝎) is the rate of change of angle during circular motion in radians /sec (𝝷/t) For a full circle 𝝎 = 2 ( T is the time period of the rotation 1/T = the frequency of rotation. f = 1/T 𝝎 = 2𝜋f Linear speed (v) and (𝝎) are linked by the equation (v = r𝝎)
The speed is always constant in the direction to the tangent at any point on the circumference but he direction is always changing towards the centre of the circle. The acceleration is always towards the centre of the circle
Centripetal acceleration towards the centre of the circle = v2/r or 𝝎2r According to Newton’s second law F = ma therefore centripetal force = mv2/r or m𝝎2r
centripetal force = mv2/r m = mass of turning object v = velocity r = radius of the turning circle
Example situation A vehicle of mass 1200kg is cornering at a velocity of 30 m/s around a level corner of radius 110m. Calculate the centripetal force exerted on the car by friction between the tyres and the road.
centripetal force = mv2/r Mass = 1200kg v = 30m/s r = 110m Centripetal force on vehicle = (1200 x 302) /110 =9818N
The vehicle is on the limit of adhesion at this velocity. Calculate the coefficient of friction between the tyres and the road (take g as 9.8m/s2).
Force(centripetal) = μ(coefficient of friction) x weight of vehicle (mass x 9.81) Weight = 1200 x 9.81 =11772N μ = Force/weight = 9818/11772 0.83
The corner now becomes banked at an angle of 12o to the horizontal. Calculate the maximum cornering velocity of the vehicle on this part of the curve.
F = mv2/r F(centripetal) = μ(coefficient of friction) x weight of vehicle (mass x 9.81) μ x m x 9.81 = mv2/r (this calculation gives us the centripetal force for cornering on a flat road) The extra centripetal force due to the 12obanking Is found by the equation m x 9.81 x tan 12o (= v2/r) v2 = (r x μ x m x 9.81)/m + (r x m x 9.81 x tan12o)/m = (r x μ x 9.81) + ( r x 9,81 x tan 12o) m’s cancel out
v2 = (r x μ x 9.81) + ( r x 9.81 x tan 12o) = (110 x 0.83 x 9.81) + (110 x 9.81x tan 12o) = 1143.8 V = √1143.8 33.8m/s
The crankshaft of a 125cc two-stroke engine carries a single piston of bore 51.5 mm and stroke 60mm. The effective rotating mass of the connecting rod and piston assembly is 200g and is out of balance with the line of the crankshaft by an eccentricity of half the stroke. The engine is running at 900 rpm. Show that this is equivalent to an angular velocity of 94.2 rad/s and calculate the centripetal force on the crankshaft bearings due to this out of balance load.
ω = angular velocity in radians/second 360o (full circle)= 2π radians ω = 2π/t (full circle) 1/t = frequency (f) ω = 2πf If the engine is running at 900rpm ω = 900 x 2π/60 = 94.2 rad/sec
v = ωr F = mv2/r = mω2r In the question m = 200g =0.2kg r = half of stroke =30 mm F = 0.2 x 94.22 x .03 = 53.24 N
The out-of-balance force on the crank is to be balanced using two identical counterweights either side of the connecting rod at an eccentricity of 0.02m. Calculate the mass of one counterweight.
m1ω2r1= 2m2ω2r2 m2 = m1r1/2r2 m1 = mass of connecting rod and piston assembly, 0.2kg r1 = half stroke, 0.03m r2 = eccentricity of counter weights, 0.02m m2 =(0.2 x 0.03)/(2 x 0.02) = 0.15 kg
Centrifugal clutch Rotating bobs springs cylinder
Rotating bobs When the angular velocity of the shaft increases the centripetal force Increases causing the springs to extend and the clearance between the bobs and the cylinder to decrease. When the centripetal force is high enough the bobs will engage with the clutch cylinder. springs cylinder
0.1m 0.01m Rotating bobs A centrifugal clutch similar to the one described has 6 rotating bobs each of mass 150g and a radius of 100mm. The spring strengths are 5kN/m Calculate the angular velocity (ω) as the bobs engage with the clutch cylinder. (The bob clearance is 0.01m and the spring length is 0.1m) springs cylinder
0.01m 0.1m Rotating bobs r = 0.1 + 0.01 = 0.11 The springs needs to extend by 0.01 m Force required = 5kN/m x 0.01 = 50N mrω2 = 50N ω2 50/(m x r) ω2 = 50/(0.15 x 0.11) springs cylinder
ω2 = 50/(0.15 x 0.11) = 3030.3 ω = 55rad/sec ω = 2πf f = ω/2π =55/2π = 8.75 rps 8.75 x 60 rpm 525 rpm
Calculate the force on the cylinder at a velocity of 1200rpm. • ω = 2πf • =7539.8 rad/min • =125.7 rad/sec • F = mrω2 • 0.15 x 0.11 x 125.72 • 261N • Net force = Centripetal force - spring force • = 261 – 50 = 211N
Explain how the coefficient of friction between the bob and the clutch face will govern the power transmitted
As ω increases the net force between the bobs and the cylinder but will always be 50N less than the centripetal force after engagement. Power transmitted will be affected by the force between the bobs and the cylinder ( F = μ x R(reaction force)) And the velocity of the clutch. As the velocity doubles the power will multiply by 4 until slip occurs