Metamorphic Rocks
230 likes | 926 Vues
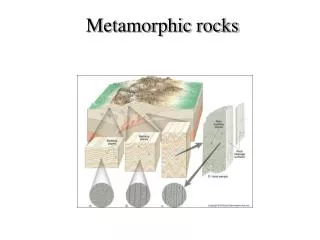
Metamorphic Rocks. C. Metamorphic Rocks. change. Metamorphism means to ______. c hanges to …. shale. gneiss. heat. pressure. Form when a rock of any type (igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic) is put under ____ and _______ to become a new metamorphic rock.

Metamorphic Rocks
E N D
Presentation Transcript
C. Metamorphic Rocks change • Metamorphism means to ______. changes to … shale gneiss
heat pressure • Form when a rock of any type (igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic) is put under ____ and _______ to become a new metamorphic rock. • The new metamorphic rock will be similar to its parent rock, but will be more _____ and less porous. dense
Foliation 90 • Identification of Metamorphic rocks: • ________: is when minerals begin to line up at a ___degree angle to the direction of the pressure. Some minerals will have moved and changed into new types.
Banding lined up bands • ________: is a type of foliation where enough minerals have ________ to make clearly visible ______. • These bands are not to be confused with the Layers of sedimentary rocks. If the rock has visible grains and particles, it is NOT metamorphic. • Metamorphic Banding will usually be curved, while Sedimentary Layers will usually be ____. flat
Banding, Foliation, or Sedimentary Layers? Banding Sedimentary Layers Foliation
Regional Metamorphism • Metamorphic rocks are formed in two ways: • _____________________: This happens under______ ________ as the rock is forced upward from the _______ of two crustal plates. This adds a great amount of ____ and _______ to the rock layers. The result is a high degree of _____________ (change). intense pressure collision heat pressure metamorphism
Quartzite Sandstone changes into _________. Limestone changes into ______. Siltstone changes into _______. Shale changes into ____, then ______, then _______, then finally ______. Marble Hornfels Slate Phyllite Schist Gneiss
Contact Metamorphism magma • ____________________: This is where an igneous intrusion (such as a ‘sill’) forces and melts its way through the layers of old rock. Where the ______ touches the other layers of rock, they become hot, changed and then _____________ by the intense _____. There is not much ________ applied here, which results in a lower metamorphic change. metamorphisize HEAT pressure