Mastering Trigonometric Identities | Essential Techniques & Examples
140 likes | 155 Vues
Learn to apply fundamental, sum & difference, double-angle, and half-angle identities to verify and find trigonometric function values efficiently. Understand Pythagorean, reciprocal, and quotient identities with helpful examples.

Mastering Trigonometric Identities | Essential Techniques & Examples
E N D
Presentation Transcript
5 Trigonometric Identities
5 Trigonometric Identities • 5.1 Fundamental Identities • 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities • 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities for Cosine • 5.4 Sum and Difference Identities for Sine and Tangent • 5.5 Double-Angle Identities • 5.6 Half-Angle Identities
Fundamental Identities 5.1 Fundamental Identities▪ Using the Fundamental Identities
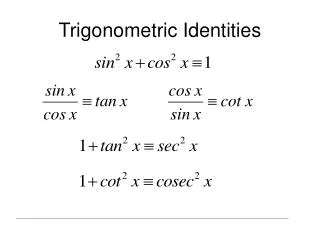
Fundamental Identities Reciprocal Identities Quotient Identities
Fundamental Identities Pythagorean Identities Negative-Angle Identities
Note In trigonometric identities, θ can be an angle in degrees, a real number, or a variable.
FINDING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTION VALUES GIVEN ONE VALUE AND THE QUADRANT Example 1 In quadrant II, sec θis negative, so • If and θ is in quadrant II, find each function value. Pythagorean identity (a) sec θ
FINDING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTION VALUES GIVEN ONE VALUE AND THE QUADRANT (continued) Example 1 from part (a) (b) sin θ Quotient identity Reciprocal identity
FINDING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTION VALUES GIVEN ONE VALUE AND THE QUADRANT (continued) Example 1 (b) cot(–θ) Reciprocal identity Negative-angle identity
Caution To avoid a common error, when taking the square root, be sure to choose the sign based on the quadrant of θ and the function being evaluated.
EXPRESSING ONE FUNCITON IN TERMS OF ANOTHER Example 2 Since sec x is related to both cos x and tan x by identities, start with • Write cos x in terms of tan x. Take reciprocals. Reciprocal identity Take the square root of each side. The sign depends on the quadrant of x.
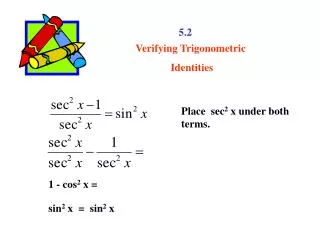
REWRITING AN EXPRESSION IN TERMS OF SINE AND COSINE Example 3 • Write in terms of sin θand cos θ, and • then simplify the expression so that no quotients appear. Quotient identities Multiply numerator and denominator by the LCD.
REWRITING AN EXPRESSION IN TERMS OF SINE AND COSINE (cont’d) Example 3 Distributive property Pythagorean identities Reciprocal identity
For example, we would not write An argument such as θ is necessary in this identity. Caution When working with trigonometric expressions and identities, be sure to write the argument of the function.