Oscillations
150 likes | 304 Vues
This resource explores fundamental concepts of oscillations involving a mass connected to a spring, addressing various possibilities during the oscillation process. Key questions include the relationships between velocity, acceleration, energy changes, and graph representations of mass dynamics. The material is designed to enhance understanding of gravitational potential energy, spring potential energy, and the effect of external forces on oscillatory systems. Utilizing clicker questions, it engages learners in critical thinking about physics concepts in a real-world context.

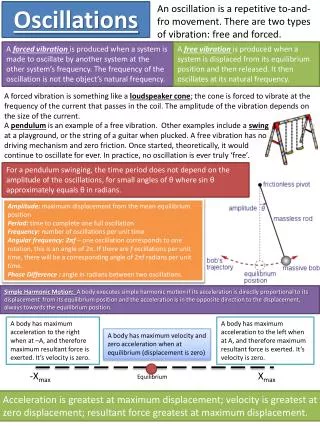
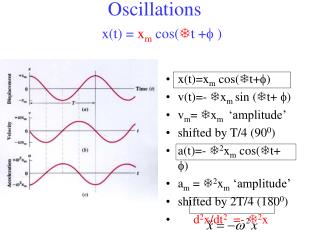
Oscillations
E N D
Presentation Transcript
A mass connected to a spring is oscillating back and forth. Consider two possibilities.Which are true?(i) at some point during the oscillation the mass has v = 0 but a ≠0 (ii) at some point during the oscillation the mass has v = 0 and a = 0 . • Both occur sometime during the oscillation. • Neither occurs during the oscillation. • Only (i) occurs. • Only (ii) occurs. NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
x x x x Tracking the motion 0 0 0 0 NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions 0 0 0 0
If curve (A) is which curve is • (A) • (B) • (C) • None of the above. NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
Which of these curvesis described by with φ > 0 (and φ<< 2π)? • (A) • (B) • (C) • None of the above. NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
When we pull the mass down from its equilibrium and release it, what happens to the energies? The gravitational PE • increases • decreases • remains the same • you can’t tell from the information given. NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
When we pull the mass down from its equilibrium and release it, what happens to the energies? The spring PE • increases • decreases • remains the same • you can’t tell from the information given. NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
When we push the mass upfrom its equilibrium and release it, what happens to the energies? The gravitational PE • increases • decreases • remains the same • you can’t tell from the information given. NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
When we push the mass upfrom its equilibrium and release it, what happens to the energies? The springPE • increases • decreases • remains the same • you can’t tell from the information given. NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
A mass is hanging from a spring. The position of the mass is measured by a sonic ranger sitting 25 cm under the mass’s equilibrium position. At some time, the mass is started oscillating. At a later time, the sonic ranger begins to take data.Which graph could represent thevelocity of the mass? NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
A mass is hanging from a spring. The position of the mass is measured by a sonic ranger sitting 25 cm under the mass’s equilibrium position. At some time, the mass is started oscillating. At a later time, the sonic ranger begins to take data.Which graph could represent thenet forceon the mass? NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
A mass is hanging from a spring. The position of the mass is measured by a sonic ranger sitting 25 cm under the mass’s equilibrium position. At some time, the mass is started oscillating. At a later time, the sonic ranger begins to take data.Which graph could represent thepotential energyof the spring? NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
A pendulum is swinging back and forth between the extremes marked A and C. At point B it is directly below the pivot. When it reaches B, the string breaks. What path will the ball follow after the break? NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
A pendulum is swinging back and forth between the extremes marked A and C. At point B it is directly below the pivot. When it reaches C, the string breaks. What path will the ball follow after the break? NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions
A pendulum swings in the plane in front of the marked board. There is a peg (indicated). When the ball passes the peg it will pivot from the peg instead of from the original pivot. How high will it go on the right? • Not as high as the 30 cm line. • Just up to the 30 cm line. • Higher than the 30 cm line. • You don’t have enough information to tell. peg NEXUS/Physics Clicker Questions