Types of Energy
80 likes | 263 Vues
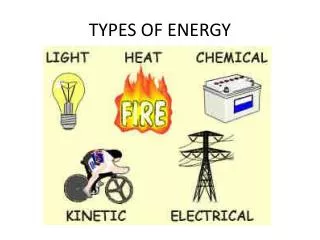
Types of Energy. -kinetic, potential, chemical and thermal -Law of conservation of energy. What is energy?. It is the ability to do work or produce heat Obeys the Law of Conservation of Energy

Types of Energy
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Types of Energy -kinetic, potential, chemical and thermal -Law of conservation of energy
What is energy? • It is the ability to do work or produce heat • Obeys the Law of Conservation of Energy • In any chemical reaction or physical process, energy can be converted from one form to another, but it is neither created nor destroyed • Called First Law of Thermodynamics
How do we measure energy? • Units • Calorie (cal) – the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of pure water by one degree Celsius • A nutritional Calorie is (Cal) • 1 Cal = 1000 cal = 1 kcal • Joule (J) – SI unit of energy and heat • 1 J = 0.2390 calories • 1 cal = 4.184 joules Example: 1 tablespoon of butter contains approximately 100 Calories. If we burn the butter to produce CO2 and H2O then 100kcal (100,000 cal) of heat would be released.
Practice • How many calories are in 45.2 J? • How many joules are in 42.4 calories?
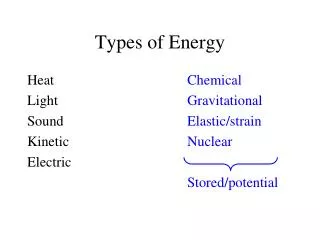
Types of Energy • Exists in two forms • Potential Energy – stored energy • Kinetic Energy – energy of motion
Potential Energy • Energy that is stored in a substance because of its composition is called chemical energy • Energy is stored in the bonds between atoms • Examples: • when plants take in radiant energy from sunlight and store it as starches and sugars
Kinetic Energy • The process of flowing from a warmer object to a cooler object is called thermal energy • The faster the particles move, the warmer the matter can get • Often represented by a q for heat • Example: • matches