Homework
210 likes | 388 Vues
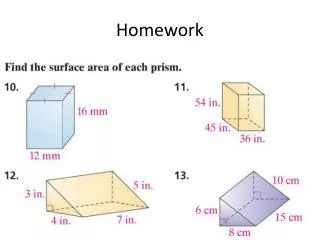
Homework. Chapter 13: 17,18,19,25,26,29,38. Review. IEEE 802.1: Internetworking IEEE 802.2: Logical link control (LLC) IEEE 802.3: CSMA/CD IEEE 802.4: Token Bus IEEE 802.5: Token Ring. Distributed Queue Dual Bus. Designed for MAN environment. It uses a dual bus configuration.

Homework
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Homework • Chapter 13: • 17,18,19,25,26,29,38
Review • IEEE 802.1: Internetworking • IEEE 802.2: Logical link control (LLC) • IEEE 802.3: CSMA/CD • IEEE 802.4: Token Bus • IEEE 802.5: Token Ring
Distributed Queue Dual Bus • Designed for MAN environment. • It uses a dual bus configuration. • Each device connects to both buses. • Access method provided by distributed queues.
Distributed Queue Dual Bus • The first station on the bus is called head bus. • The last station on the bus is called end bus. • Traffic on each bus is unidirectional (from head bus toward end bus). • Direction of the flow of data determines whether stations are upstream or downstream relative to a particular station.
Medium Access Method • The head of each bus generates 53-byte empty slots for use on its bus. • The receiving device must be downstream of the transmitting device (The source station must decide which bus to use).
Medium Access Problem • The stations closer to head bus may monopolize the medium (they see the empty slot first).
Solution to Medium Access Problem • Slot Reservation: • Does this solve the problem? • No? • How would stations upstream know of the reservation made by downstream stations?
Solution to Medium Access Problem • How would stations upstream know of the reservation made by downstream stations? • To send data on one bus, a station must use the other bus to make a reservation.
Keeping Track of Reservations • Each station stores two queues (One for each bus). • Queue A for bus A • Queue B for bus B
Alternate Configuration For DQDB • DBDQ can be used in Ring Configuration. • One station plays the roles of both header and end station.
Connecting LANs using T-Lines Dedicated lines (expensive) May not be used efficiently
Switched Multimegabit Data Services (packet-switched datagram service)
Features of SMDS • Can be used as a backbone network connecting multiple LANs. • It is a switched-packet network (you pay only when you use the network) • Supports frames of up to 9188 bytes. • Data rate ranges from 1.544 Mbps to 155 mbps. • It supports multicasting. • It uses telephone numbers for addressing • 15 digits=country code+ area code +subscriber number