Atoms, formulas and equations
170 likes | 345 Vues
Atoms, formulas and equations. Learning Objectives. Know the properties of mixtures and compounds Explain how atomic structure relates to the Periodic Table Show how atomic structure enables chemical bonding and rearrangement of atoms to form new substances. Mixtures. Mixtures.

Atoms, formulas and equations
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Learning Objectives • Know the properties of mixtures and compounds • Explain how atomic structure relates to the Periodic Table • Show how atomic structure enables chemical bonding and rearrangement of atoms to form new substances
Mixtures • Easily separated • No chemical bonds • Can be separated physically e.g. heating , as in distillation • Examples of mixtures are: • a)Iron filings powder and sulfur powder • b)crude oil
Compounds • Atoms join together to form compounds, by giving, taking or sharing electrons • This holds the compound together with chemicalbonds • Bonding is a chemical reaction. No atoms are created or destroyed, only rearranged
Chemical Reactions • Only electrons in the outer shell of the atom are involved Opposites attract : +ve and –ve Chemical reactions depend on this Some reactants need heat for a reaction to take place Atoms are the same at the end of the chemical reaction, but in a different arrangement
Reactants and Products • Some energy is “lost” in every chemical reaction , because of the movement of the atoms during the chemical process • Yield is never 100%
Molecular Weight • Atoms have a Mass Number • The relative mass of an element is known as the MOLE of that substance • The mole is given in grams. • 1 mole = relative atomic mass of any substance expressed in grams
The Periodic Table • All substances consist of atoms. • An element is a substance made from one type of atom only • There are about 100 elements in the Periodic table arranged to show: • Groups (vertical) elements with the same properties • Periods (horizontal)arranged in order of atomic number
Key Words • Electrons compounds bonds mixtures equation ionic covalent mole formulas
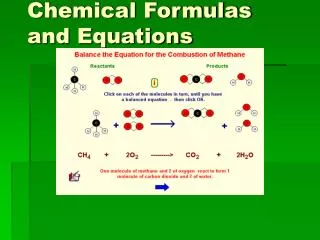
Balancing Equations The number of atoms on the left should equal the number of atoms on the other side Bonds are broken and reformed
Bleach is addedto swimming pools to kill harmful bacteria. • Getting the quatities right is checked every day. • When chlorine gas is pumped through a solution of sodium hydroxide dissolved in water: • Sodium hydroxide + chlorine –> bleach + salt + water