Modular Arithmetic Warmup
30 likes | 188 Vues
This article delves into the concepts of modular arithmetic, focusing on computing powers and discrete logarithms. We calculate ( 32 mod 7 ) and ( 325 mod 7 ), revealing intriguing results like ( 32 equiv 2 mod 7 ) and ( 325 equiv 3 mod 7 ). We also explore the relationship between logarithms in modular contexts, including how to find discrete logarithms, like determining ( log_{123} 1 mod 7 ). With practical examples and solutions, we uncover the complexity and elegance of modular computations.

Modular Arithmetic Warmup
E N D
Presentation Transcript
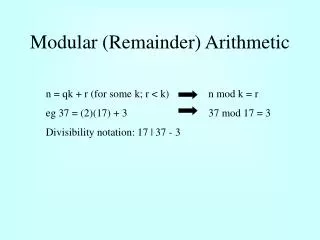
Computing powers What is 32 (mod 7)? 32 = 9 = 2 (mod 7) What is 325 (mod 7)? 325 = (312)2×3 312 = (36)2 36 = (33)2 33 = 32×3 = 2×3 = 6 (mod 7) 36 = 62 = 1 (mod 7) 312 = 12 = 1 (mod 7) 325 = 12 × 3 = 3 (mod 7)
Discrete Logarithms • So 25 is a base-7 discrete logarithm of 3 since 325 = 3 (mod 7) • What is log123133226724974042726916099225072978121787999602681264220242808237393822637462751150704898781659019329899261348951831735003? • Easy using Wolfram alpha: • logba = log a/log b • But what is a discrete base 123 log of 1 (mod 7)? • 57 is an answer since 12357 = 19032389282006103845157032153282588826857086097323460034686891056260376780393021529271254522717047128465906993118819286×7+1 • But how would you ever know? • And if the base and the modulus get bigger ….