Acceleration and Speed Changes in Physics
110 likes | 147 Vues
Explore the concept of acceleration in physics, including its definition, practice problems, speed vs. time graphs, and how acceleration relates to changes in speed and direction. Learn about positive and negative acceleration and how to interpret speed vs. time graphs.

Acceleration and Speed Changes in Physics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Acceleration Chapter 2.4
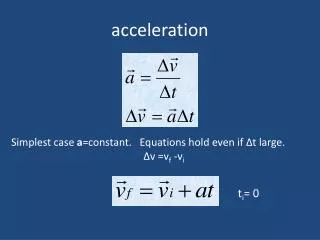
acceleration • Rate at which velocity is changing acceleration= change of velocity time Acceleration = change of speed (along a straight line) time
Acceleration occurs when there is either a change in speed, change in direction or both (whenever there is a change in velocity).
In physics, acceleration applies to both increases and decreases in speed • Decrease in speed= negative acceleration
Practice Problem • Suppose a car moving in a straight line steadily increases its speed each second, first from 35 to 40 km/h, then from 40 to 45 km/h, them from 45 to 50 km/h. What is its acceleration? • Speed increases 5 km/h each 1 s interval, therefore acceleration= 5 km/h*s (read 5 km per hour second)
Practice Problem 2 • In 5 seconds a car moving in a straight line increases its speed from 50 km/h to 65 km/h, while a truck goes from rest to 15 km/h in a straight line. Which undergoes the greater acceleration? What is the acceleration of each vehicle? • Acceleration for both vehicles is 15 km/h*s (the undergo the same acceleration even though their speeds are quite different)
Speed vs. Time Graphs • X axis: always time • Y axis: always speed • Slope of line = speed/time • Slope tells you what happens to acceleration of the object • Area under line tells you the distance the object traveled.
What is happening in this graph? • Objected started at rest • Speed is increasing • Object is accelerating
What is happening in this graph? • Object is slowing down • Object is negatively accelerating (decelerating)
What is happening in this graph? • Both objects are moving • Both objects are increasing speed but at different rates • Dashed line increases speed faster so it has the greater acceleration