Trigonometry
90 likes | 217 Vues
This guide provides an overview of angles, degrees, and special triangles in trigonometry. It defines what constitutes an angle, addressing counterclockwise and clockwise rotations and their respective designations as positive or negative angles. The document covers key concepts like complementary and supplementary angles, and introduces the Pythagorean Theorem, highlighting the relationship between the legs and hypotenuse of right triangles. Special triangles, such as the 30-60-90 and 45-45-90 triangles, are discussed with their unique angle measures and side ratios.

Trigonometry
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Trigonometry 1.1 Angles, Degrees, and Special Triangles
An angle is formed by two rays with a common vertex. • Every angle has an initial and terminal side. • Counterclockwise rotation from initial to terminal side results in a positive angle • Such a rotation that is clockwise results in a negative angle. Angles in General
Degree- • Complementary- • Supplementary- Degree Measure
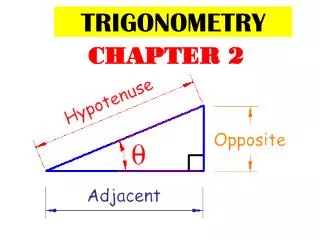
For any right triangle, the sum of the squares of the legs equals the square of the hypotenuse. • Proof: See page 5 of text. Pythagorean Theorem
Memorize this relationship. 30-60-90 Triangles 60° 2x x 90° 30° x
45-45-90 Triangles 45° x x 45° x
Open the Socrative Student App, go to room #60306. Question 3 45° 10 m Quiz Questions 45° Question 4 60° 8 90° 30° y
Page 10: 1-65 odds Assignment