Scaffold User in Construction
360 likes | 738 Vues
Scaffold User in Construction. Learning Objectives. Objectives: OSHA Standard for Scaffold users, 29 CFR 1926.454(a) Procedures for dealing with Hazards Proper use of scaffolds Proper material handling. Agenda. Agenda: Overview Scaffold types Terminology Associated hazards Proper use

Scaffold User in Construction
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Learning Objectives • Objectives: • OSHA Standard for Scaffold users, 29 CFR 1926.454(a) • Procedures for dealing with Hazards • Proper use of scaffolds • Proper material handling
Agenda • Agenda: • Overview • Scaffold types • Terminology • Associated hazards • Proper use • Your responsibilities
Section 1 Overviewof the Issue
Scaffold Use in Construction • Scaffold prevention: • 4500 injuries annually • 50 deaths annually • $90 million in workdays
Categories • Three major scaffolds: • Supported • Suspended • Other
What does OSHA have to say? • Key elements: • Fall protection, fall arrest systems • Guardrail height • Crossbracing, midrails and footings • Platforms, guying ties, and capacity • Training • Inspections • Erecting and dismantling
The Competent Person • Duties include: • Select and direct employees • Determine safe work conditions • Training • Inspections
The Qualified Person • Duties include: • Design and load scaffold • Training • Design rigging for suspension scaffolds • Design platforms less than 36”
Engineer • Must design: • Direct connection of mason’s multi-point adjustable suspension scaffolds • Pole scaffolds over 60 feet tall • Tube and coupler scaffolds over125 feet tall
Employee Training • Training includes: • Electrical, fall, and falling objects hazards • How to deal with hazards • Proper use of scaffolds • Maximum intended load • Other pertinent information
Section 2 Types of Scaffolds
Types of Scaffolds • Scaffolds: • Over 25 different types in use • Most common include fabricated, supported frame or system scaffolds
Types of Scaffolds • Scaffolds: • Plasterers’, decorators, and large area scaffolds • Bricklayers square scaffolds • Horse scaffolds • Form scaffolds • Roof bracket scaffolds • Outrigger scaffolds (one level) • Pump and window jack scaffolds
Types of Scaffolds • Scaffolds: • Step, platform and trestle ladder • Single point adjustable suspension • Two point adjustable suspension • Catenary scaffolds • Float (ship) scaffolds • Interior hung scaffolds
Types of Scaffolds • Scaffolds: • Needle beam scaffolds • Multi-level suspension scaffolds • Mobile scaffolds • Repair bracket scaffolds • Stilts • Tank builder scaffolds
Types of Scaffolds • Scaffolds: • Many different scaffolds in workplace • Choice is based on work to be performed • Erection done only b trained professional
Section 3 Scaffold Terminology
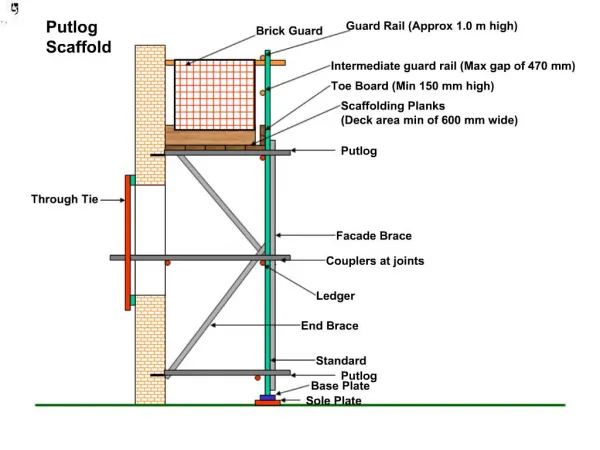
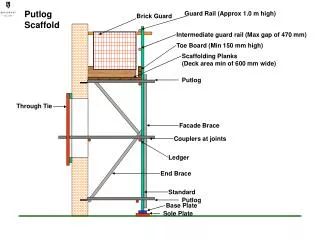
Scaffold Terminology • Terminology: • What is a scaffold? • What is a platform? • What is a brace? • What is a stair tower? • What is a runner, ledger or ribbon? • What is a bearer? • What are mud sills and base plates?
Scaffold Terminology • Terminology: • What is a scaffold Competent Person? • What is a scaffold Qualified Person? • What is the Maximum Intended Load? • What is a Rated Load?
Section 4 Hazards Associated with Scaffold Use
Hazards Associated with Scaffold Use • Hazards: • Electrical hazards • Fall hazards • Falling objects
Electrical Hazards – Overhead Power Lines • Clearance for insulated lines: • <300v = minimum 3 feet • 300v to 50kv = minimum 10 feet • >50kv = 10 feet + .4 inches for each kv over 50 • Clearance for non-insulated lines: • Less than 50kv = minimum 10 feet • >50kv = 10 feet + .4 inches for each kv over 50
Fall Hazards • Protection: • Install guardrails • Employ use of harness and lanyard (personal fall arrest system)
Fall Hazards • Guardrail systems: • Height between 38 and 45 inches • Withstand 200 pounds of force
Falling Objects Protection Systems • Falling objects protection: • Hard hats • Toe boards • Safety screens or guardrails • Debris nets, catch platforms, or canopy structures
Section 5 Proper Use of Scaffolds
Proper Use of Scaffolds • Basic ground rules: • Never overload scaffolds • Always inspect scaffolds prior to use • Repair, replace, or remove from service • Competent or qualified individual supervises the erection, installation, repair, or relocation of scaffolds
Basic Safety Issues for Work on Scaffolds • Be aware of: • Weather conditions • Debris • Makeshift devices to gain height • Ladders in use on platforms • Load within capacity of scaffold
What is Wrong with this Picture? • What do you think of this scaffold design? • Planks not cleated or secured • No guardrails • Greater than 14 inch gap between scaffold and building
What is Wrong with this Picture? • What do you think? • No midrails • No toeboards • No mesh • Safety lines not tied to proper anchorage
Section 6 Your Responsibilities
Your Responsibilities • You should: • Understand power lines within 10 feet • Appropriate scaffolding inspection • Properly install mud sills and base plates • Guardrails and platforms secured in place • Conditions of decking or planks
Your Responsibilities • Also: • Know the maximum intended load for each unit • Know debris removal policy while on scaffolds • Monitor weather conditions • Worker training