Mastering Angles: Geometry Basics & Measurements
100 likes | 184 Vues
Learn about angles in geometry, from naming to measuring. Understand types like acute, right, obtuse, and straight angles. Discover angle bisectors and congruent angles. Practice examples using angle addition postulate. Ideal for students!

Mastering Angles: Geometry Basics & Measurements
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Geometry 1-3 Measuring and Constructing Angles
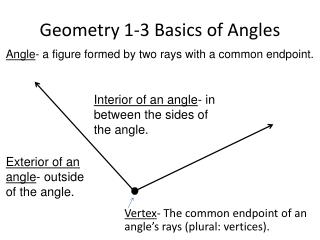
Vocabulary • Angle- a figure formed by two rays, or sides, with a common endpoint. • Vertex- The common endpoint of an angle (plural: vertices). • Interior of an angle- all points between the sides of an angle. • Exterior of an angle- all points outside of the sides of an angle. • Degree- the unit of measure for angles.
Naming Angles • Angles can be named three ways: • By its vertex R • By a number 1 • By a point on each ray and the vertex SRT or TRS S 1 R T
Name the Marked Angle W 2 A R L
Types of Angles • Acute angle: 1° to 89 ° • Right angle: 90 ° • Obtuse angle: 91 ° to 179 ° • Straight angle: 180 °
More Vocab. • Congruent angles- angles that have the same measure. • Angle bisector- A ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles Congruent angles: ARW LRW Angle bisector: RW W A R L 45° 45°
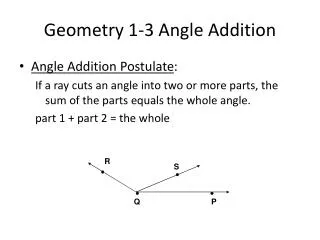
Postulate • Angle Addition Postulate: If S is in the interior of PQR, then m PQS + m SQR = m PQR (part 1 + part 2 = the whole) R S Q P
Example • What is the measure of angle WRL? W T A 65° R L 45°
Example • If Y is in the interior of LMN, find the m LMY if m LMY = 5x+3, m YMN = 3x+3, and m LMN=86°.
Using a Protractor wxv zxw YXZ