Primitive Values Vs Objects
170 likes | 335 Vues
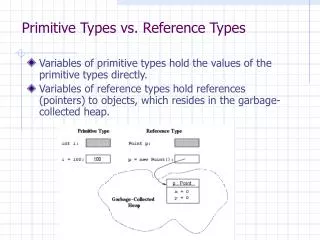
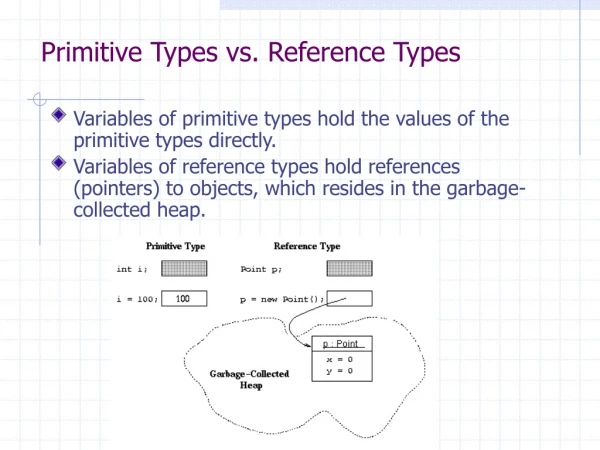
Primitive Values Vs Objects. Wrapper Classes Memory Representation of Primitive Values Vs Objects Pointers Equal Vs == Sharing of Objects Garbage Collection. Number. Double. Integer. wrapper class. wrapper class. Wrapper Classes. “Joe Doe”.toString(). Object.

Primitive Values Vs Objects
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Primitive Values Vs Objects • Wrapper Classes • Memory Representation of Primitive Values Vs Objects • Pointers • Equal Vs == • Sharing of Objects • Garbage Collection
Number Double Integer wrapper class wrapper class Wrapper Classes “Joe Doe”.toString() Object Vector vector = new Vector() vector.addElement(“Joe Doe”) (new Integer(5)).toString() new Integer(5) 5 String AStringHistory vector.addElement(new Integer(5)) vector.elementAt(3).intValue() vector.elementAt(3) AStringDatabase 5.toString() char boolean double int vector.addElement(5)
Other Wrapper Classes • Double • public Double(double value) • publicdouble doubleValue() • Boolean • public Boolean(boolean value) • publicboolean booleanValue() • Character • public Character(char value) • publicchar charValue() • Float, Short, Long
8 5.5 5.5 memory address 5 16 5 48 double d same size int i 52 same, double size double e 80 Storing Primitive Values/Variables int i = 5; 5.5 double d = 5.5; 5 double e = d; 5.5
8 5.5 Double@8 16 5 Integer@16 48 Double D different sizes memory address 60 Integer I variables same size Storing Objects Values/Variables Integer I = new Integer(5) Double D = new Double(5.5) 8 16
Structured Objects • publicclass APoint implements Point { • int x, y; • public APoint (int initX, int initY) { • x = initX; y = initY; • } • publicint getX() {return x}; • publicvoid setX(int newVal) {x = newVal;} • publicint getY() {return y}; • publicvoid setY(int newVal) {y = newVal;} • }
8 5.5 Double@8 16 5 Integer@16 48 Double D 60 Integer I 80 50 APoint@80 100 96 Point p Structured Objects publicclass APoint implements Point { // instance vars int x, y; //methods … } 16 Point p = new APoint(50, 100) 80
Superclass Constructor Inheritance • publicclass ABoundedPoint extends APoint { • APoint upperLeftCorner, lowerRightCorner; • public ABoundedPoint (int initX, int initY, Point initUpperLeftCorner, Point initLowerRightCorner) { • super(initX, initY); • upperLeftCorner = initUpperLeftCorner; • lowerRightCorner = initLowerRightCorner; • } • … • } • }
8 50 APoint@8 50 16 100 APoint@16 100 ABoundedPoint@48 48 75 75 publicclass APoint implements Point { int x, y; … } Inheritance publicclass ABoundedPoint extends APoint { PointupperLeftCorner ; PointlowerRightCorner; … } 8 16 new ABoundedPoint(75, 75, new APoint(50,50), new APoint(100,100))
16 Point p1 P1 P2 48 Point p2 APoint@8 Assignment of Object Variables Point p1 = new APoint(50, 50); 8 50 APoint@8 Point p2 = p1; 50 p1.setX(100); 8 8
P1 P2 48 Point p2 APoint@8 Assignment of Object Variables Point p1 = new APoint(50, 50); 8 100 APoint@8 Point p2 = p1; 50 p1.setX(100); p2.getX() 100 16 8 Point p1 p1 = new APoint(200,200); 8
P1 P2 APoint@64 APoint@8 Assignment of Object Variables Point p1 = new APoint(50, 50); 8 100 APoint@8 Point p2 = p1; 50 p1.setX(100); p2.getX() 100 16 64 Point p1 p1 = new APoint(200,200); p2.getX() 100 p2 = p1; 48 8 Point p2 64 200 APoint@64 200
P1 P2 APoint@64 APoint@8 Garbage collected Assignment of Object Variables Point p1 = new APoint(50, 50); 8 100 APoint@8 Point p2 = p1; 50 p1.setX(100); p2.getX() 100 16 64 Point p1 p1 = new APoint(200,200); p2.getX() 100 p2 = p1; p2.getX() 200 48 64 Point p2 64 200 APoint@64 200
Same physical object? P1 P2 APoint@64 APoint@8 == for Objects Point p1 = new APoint(200, 200); 8 200 APoint@8 Point p2 = new APoint(200, 200) 200 p2 == p2 false 16 64 Point p1 48 8 Point p2 64 200 APoint@64 200
P1 P2 APoint@8 == for Objects Point p1 = new APoint(200, 200); 8 200 APoint@8 Point p2 = p1; 200 p2 == p2 true 16 8 Point p1 48 8 Point p2
S1 S2 String@64 String@8 == Vs Equal for Strings String s1 = “Joe Doe”; 8 Joe Doe String@8 String s2 = “Joe Doe” s1 == s2 false 16 64 String s1 s1.equals(s2) true 48 8 String s2 64 Joe Doe String@64
p2 == p2 false p1.equals(p2) true == Vs equals() for Objects Point p1 = new APoint(200, 200); 8 200 APoint@8 Point p2 = new APoint(200, 200) 200 16 64 Point p1 48 8 Point p2 64 200 APoint@64 publicboolean equals(Point otherPoint) { return x == otherPoint.getX() && y == otherPoint.getY(); } 200