VPNs
120 likes | 554 Vues
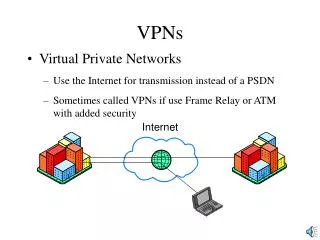
VPNs Virtual Private Networks Use the Internet for transmission instead of a PSDN Sometimes called VPNs if use Frame Relay or ATM with added security Internet VPNs Why use the Internet? Inexpensive Business partners are already connected to the same network (the Internet)

VPNs
E N D
Presentation Transcript
VPNs • Virtual Private Networks • Use the Internet for transmission instead of a PSDN • Sometimes called VPNs if use Frame Relay or ATM with added security Internet
VPNs • Why use the Internet? • Inexpensive • Business partners are already connected to the same network (the Internet) • May use different PSDNs, but everybody is connected to the Internet
VPNs • Problems with the Internet • Congestion: slows transmissions • Reliability: cannot always connect, sometimes fails during transmissions • Lack of security
VPNs • IETF developing IPsec security standards • IP security • At the internet layer • Protects all messages at the transport and application layers E-Mail, WWW, Database, etc. TCP UDP IPsec
VPNs • IPsec Transport Mode • End-to-end security for hosts Local Network Internet Local Network Secure Communication
VPNs • IPsec Tunnel Mode • IPsec server at each site • Secure communication between sites Local Network Internet Local Network IPsec Server Secure Communication
VPNs • IPsec Modes Can be Combined • End-to-end transport mode connection • Within site-to-site tunnel connection Local Network Internet Local Network Tunnel Mode Transport Mode
VPNs • Another Security System for VPNs is the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) • For dial-up connections, based on PPP • Connects user with securely to a remote access server at a site Dial-Up Connection Local Network Internet PPTP Connection Remote Access Server
Virtual Private Networks • Other Problems Remain • Internet Congestion is Still a Problem • Internet throughput tends to be low • Internet Reliability is Low • Cannot get connections • Backbone fails occasionally
Virtual Private Networks • Alternative • Avoid the congested and unreliable backbone! • Use one ISP that serves all sites • Should offer QoS service level agreement (SLAs) for latency and reliability Site 1 ISP Site 2
Virtual Private Networks • Alternative • Avoid the congested backbone • Use ISPs that “peer” with one another: connect with one another not through the Internet backbone • May offer end-to-end SLAs Site 1 ISP A ISP B Site 2 Peering
WANs in Perspective • Both Leased Line Networks and PSDNs are widely used and will be for several years to come • Leased Line Networking is shrinking while PSDN networking is growing rapidly • VPN technology and standards are still immature and use will be very low for several years to come