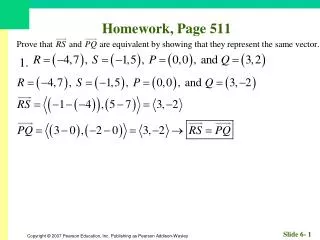
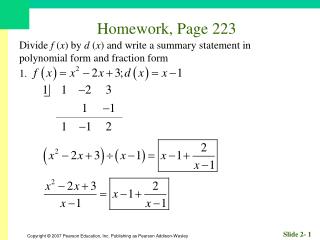
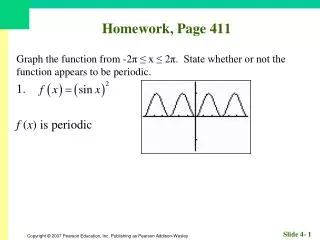
Homework, Page 55
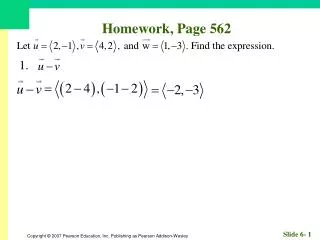
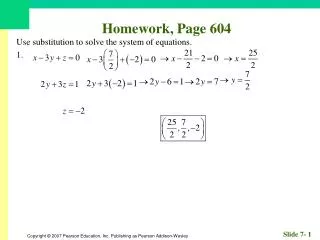
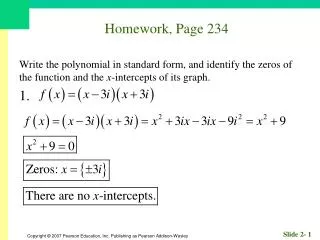
560 likes | 889 Vues
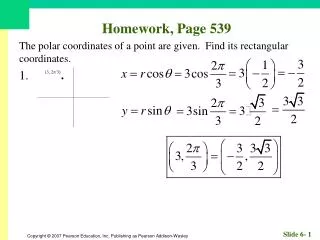
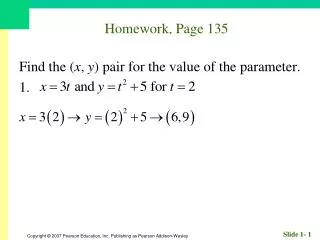
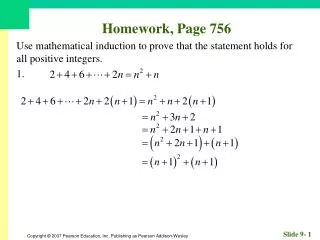
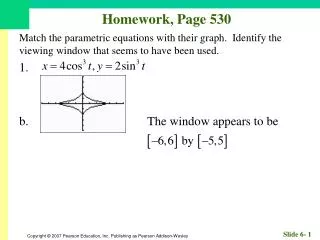
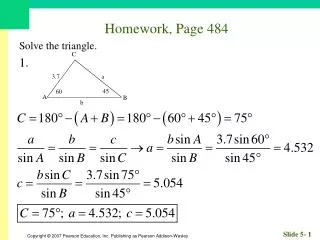
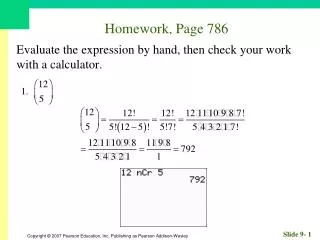
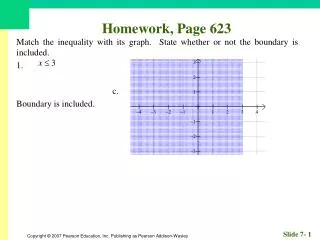
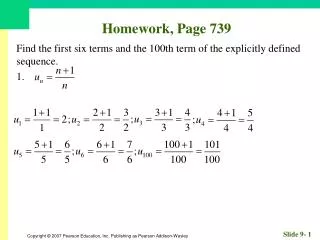
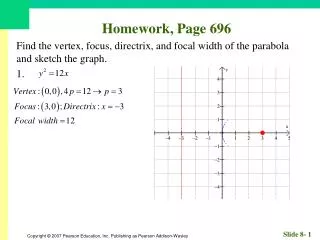
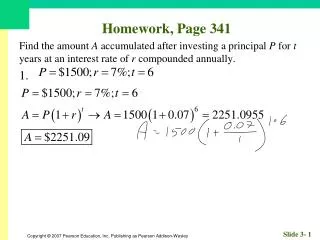
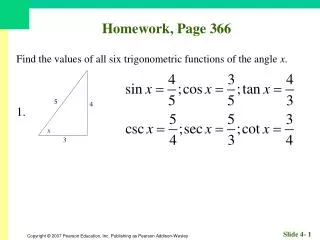
Homework, Page 55. Find an equation for each circle. 1. Center (–2, 3); radius 3. Homework, Page 55. Find an equation for each circle. 3. Center (0, 3); radius 12. Homework, Page 55. Graph, if possible. Find center and radius. 5. . Homework, Page 55.

Homework, Page 55
E N D
Presentation Transcript
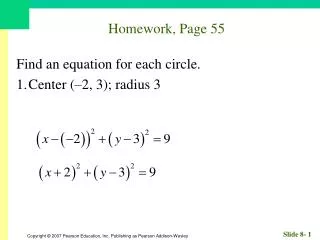
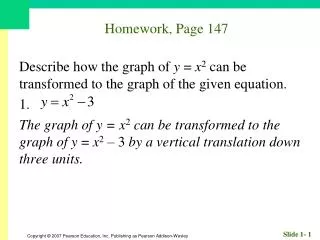
Homework, Page 55 Find an equation for each circle. 1. Center (–2, 3); radius 3
Homework, Page 55 Find an equation for each circle. 3. Center (0, 3); radius 12
Homework, Page 55 Graph, if possible. Find center and radius. 5.
Homework, Page 55 Graph, if possible. Find center and radius. 7.
Homework, Page 55 Graph, if possible. Find center and radius. 9.
Homework, Page 55 Graph, if possible. Find center and radius. 11.
Homework, Page 55 Graph, if possible. Find center and radius.13. Empty graph.
Homework, Page 55 Graph, if possible. Find center and radius.15.
Homework, Page 55 Find an equation of the line tangent to the circle at P. 17.
Homework, Page 55 Determine if A is inside, on, or outside the circle. 19. C = (2, –1); r = 3; A = (3, 2)
Homework, Page 55 Determine if A is inside, on, or outside the circle. 21. C = (0, 0); r = 4; A = (2, 2)
Homework, Page 55 Find an equation of each circle. 23. Center (3, 5); tangent to the x-axis
Homework, Page 55 Find an equation of each circle. 25. Tangent to the x-axis, the y-axis, and the line y = 5. (two answers)
Homework, Page 55 Find an equation of each circle. 27. Center on the line y = 1 – 2x, tangent to the y-axis at (0, 3)
Homework, Page 55 29. Find an equation of the circle containing (–9, 2), (–1, 2), (–1, 6), and (–9, 6)
8.1 Conic Sections and Parabolas
What you’ll learn about • Conic Sections • Geometry of a Parabola • Translations of Parabolas • Reflective Property of a Parabola … and why Conic sections are the paths of nature: Any free-moving object in a gravitational field follows the path of a conic section.
Parabola A parabola is the set of all points in a plane equidistant from a particular line (the directrix) and a particular point (the focus) in the plane.
Parabolas with Vertex (0,0) • Standard equation x2 = 4pyy2 = 4px • Opens Upward or To the right or to the downward left • Focus (0,p) (p,0) • Directrix y = –p x = –p • Axis y-axis x-axis • Focal length pp • Focal width |4p| |4p|
Parabolas with Vertex (h,k) • Standard equation (x–h)2 = 4p(y–k)(y–k)2 = 4p(x–h) • Opens Upward or To the right or to the downward left • Focus (h,k+p) (h+p,k) • Directrix y = k–px = h–p • Axis x = h y = k • Focal length pp • Focal width |4p| |4p|
Example Solving a word Problem About Parabolas 62. Stein Glass, Inc. makes parabolic headlights for a variety of automobiles. If one of its headlights has a parabolic surface generated by the parabola x2 = 12y, where should the light bulb be placed?
Homework • Homework Assignment #21 • Review Section: 7.1 • Page 641, Exercises: 1 – 69 (EOO)
8.2 Ellipses
What you’ll learn about • Geometry of an Ellipse • Translations of Ellipses • Orbits and Eccentricity • Reflective Property of an Ellipse … and why Ellipses are the paths of planets and comets around the Sun, or of moons around planets.
Ellipse An ellipse is the set of all points in a plane whose distance from two fixed points in the plane have a constant sum. The fixed points are the foci (plural of focus) of the ellipse. The line through the foci is the focal axis. The point on the focal axis midway between the foci is the center. The points where the ellipse intersects its axis are the vertices of the ellipse.
Ellipse - Additional Terms The major axis is the chord connecting the vertices of the ellipse. The semimajor axis is the distance from the center of the ellipse and to one of the vertices. The minor axis is the chord perpendicular to the major axis and passing through the center of the ellipse. The semiminoraxis is the distance from the center of the ellipse to one end of the minor axis, sometimes called a minor vertex.