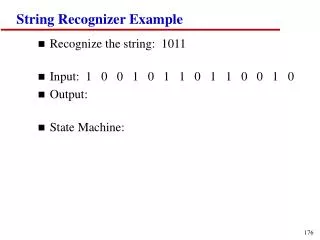
String Recognizer Example
310 likes | 772 Vues
String Recognizer Example. Recognize the string: 1011 Input: 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 Output: State Machine:. String Recognizer Example (cont.). State Table:. String Recognizer Example (cont.). Implementation:. FSMs & Flip Flops.

String Recognizer Example
E N D
Presentation Transcript
String Recognizer Example • Recognize the string: 1011 • Input: 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 • Output: • State Machine:
String Recognizer Example (cont.) • State Table:
String Recognizer Example (cont.) • Implementation:
FSMs & Flip Flops • Sometimes may be more efficient to implement FSM with other Flip Flops that Dff • Approach: • Given state table & Flip Flop Excitation table, determine how to use Flip Flop for this circuit J-K Excitation Table:
Parity with J-K (cont.) • Implementation:
Parity with T T Excitation Table:
Vending Machine with J-K J-K Excitation Table:
FSM Word Problem: Traffic Light Controller A busy highway is intersected by a little used farmroad. Detectors C sense the presence of cars waiting on the farmroad. With no car on farmroad, light remain green in highway direction. If vehicle on farmroad, highway lights go from Green to Yellow to Red, allowing the farmroad lights to become green. These stay green only as long as a farmroad car is detected but never longer than a set interval. When these are met, farm lights transition from Green to Yellow to Red, allowing highway to return to green. Even if farmroad vehicles are waiting, highway gets at least a set interval as green. Assume you have an interval timer that generates a short time pulse (TS) and a long time pulse (TL) in response to a set (ST) signal. TS is to be used for timing yellow lights and TL for green lights.
Traffic Light Controller (cont.) Picture of Highway/Farmroad Intersection:
Traffic Light Controller (cont.) • Tabulation of Inputs and Outputs: Input Signal reset C TS TL Output Signal HG, HY, HR FG, FY, FR ST Description place FSM in initial state detect vehicle on farmroad short time interval expired long time interval expired Description assert green/yellow/red highway lights assert green/yellow/red farmroad lights start timing a short or long interval • Tabulation of Unique States: Some light configuration imply others Description Highway green (farmroad red) Highway yellow (farmroad red) Farmroad green (highway red) Farmroad yellow (highway red) State S0 S1 S2 S3
Traffic Light Controller (cont.) • State Diagram
Traffic Light Controller (cont.) • State Table using J-K Flip Flops
Registers • Storage unit. Can hold an n-bit value • Composed of a group of n flip-flops • Each flip-flop stores 1 bit of information • Normally use D flip-flops D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk
Controlled Register D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk
Out In D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk Clock Shift Register • Register that shifts the binary values in one or both directions
D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk Transfer of Data • 2 modes of communication: Parallel vs. Serial • Parallel: all bits transferred at the same time • Serial: one bit transferred at a time • Shift register can be used for serial transfer
Shift Register w/Parallel Load D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk
Bidirectional Shift Register w/Parallel Load D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk D Q Dff clk
Conversion between Parallel & Serial LSI LSI D3 Q3 4-bit D2 Q2 Shift D1 Q1 Reg. D0 Q0 Shift Load Clk D3 Q3 4-bit D2 Q2 Shift D1 Q1 Reg. D0 Q0 Shift Load Clk
Counters • A reg. that goes through a specific state sequence • n-bit Binary Counter: counts from 0 to 2N-1 in binary • Up Counter: Binary value increases by 1 • Down Counter: Binary value decreases by 1 • 3-bit binary up counter state diagram:
Arbitrary Sequence Counters • Design a 3-bit count that goes through the sequence 000->010->100->101->111->110->001->011->000->...
Memory • Need method for storing large amounts of data • Computer programs, data, pictures, etc. • RAM: Random Access Memory, Read/Write • ROM: Read-only Memory 64x8 RAM A3 D7 A2 D6 A1 D5 A0 D4 D3 D2 D1 Write D0
000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111 3:8 Decoder Enable S2 S1 S0 8x4 RAM In3 In2 In1 In0 Write A2 A1 A0 Out3 Out2 Out1 Out0
RAM Cell • Requirements: • Store one bit of data • Change data based on input when row is selected Input S Q R Row Select
RAM Expansion • Implement a big RAM from multiple small RAMS D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Address 0000000 0010000 0100000 0110000 1000000 1010000 1100000 1110000
RAM Expansion (cont) • Build a 16x16 RAM from 16x4 RAMs 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write
RAM Expansion (cont) • Build a 32x16 RAM from 16x4 RAMs 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write 16x4 RAM A3 Din A2 A1 Dout A0 Write