Understanding Polynomial Theorems: Roots, Rationality, and Sign Changes
70 likes | 191 Vues
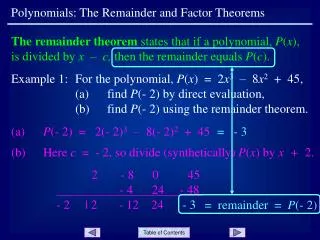
This guide delves into essential theorems related to polynomials, elucidating concepts such as Descartes' Rule of Signs, which determines the number of positive and negative real roots based on sign changes. The Rational Root Theorem identifies potential rational roots using coefficients, while the principles governing irrational and imaginary roots reveal their pairing in conjugates. Additionally, the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra asserts that a polynomial's roots match its degree, and the Remainder Theorem clarifies that the remainder of a polynomial divided by (x-a) equals its evaluated value at 'a'.

Understanding Polynomial Theorems: Roots, Rationality, and Sign Changes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The number of sign changes tells us the number of positive and negative real roots of a polynomial. Descartes Rule of Signs
p/q tells the possible rational roots of a polynomial where p is the constant and q is the beginning coefficient Rational Root Theorem
Irrational Roots come in conjugate pairs Irrational Root Theorem
Imaginary roots come in complex conjugate pairs Imaginary Root Theorem
The number of roots of a polynomial is equal to its degree Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
The remainder when dividing a polynomial by (x-a) is the value of that polynomial at “a” The Remainder Theorem