WATER
360 likes | 658 Vues
WATER. Can a needle float in water?. Surface Tension. The Extraordinary Properties of Water. 3 States of Water. Liquid, Solid and Gas. Water is the only substance found naturally on the Earth’s surface as a solid, liquid and gas all at one time!. H. H. Water.

WATER
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Can a needle float in water? Surface Tension
The Extraordinary Properties of Water 3 States of Water Liquid, Solid and Gas .
Water is the only substance found naturally on the Earth’s surface as a solid, liquid and gas all at one time!
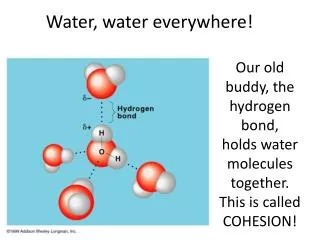
H H Water • A water molecule (H2O), is made up of threeatoms --- one oxygenand two hydrogen. δ+ δ+ δ- O
Water is Polar What type of bond do water molecules form? Polar Covalent
Hydrogen Bonding • The ends of polar molecules attract each other and can form Hydrogen Bonds. Hydrogen Bonds are intermolecular not atomic and are very important in nature.
Covalent Bond Hydrogen Bond Do you recognize this molecule?
Properties of Water • At sea level, pure water boils at 100 °C and freezes at 0 °C.
Properties of Water • Cohesion • Adhesion • Surface Tension • Capillary Action
Cohesion • Attraction between particles of the same substance (why water is attracted to itself) • Results in Surface tension (a measure of the strength of water’s surface) Water Strider
Adhesion • Attraction between two different substances. • Water will make hydrogen bonds with other surfaces such as glass, soil, plant tissues, and cotton. This is how water makes things “wet.”
ADHESION COHESION
Capillaryaction • Capillaryaction -water molecules will • “ pull ” each other along when in a thin tube.
Transpirationprocess which plants and trees remove water from the soil and carry up to the leaves. • As one water molecule evaporates, the hydrogen bonds pull the next one up.
Heat Capacity (High) • Water changes temp very slowly because it can store heat. • This protects living organisms from the shock of abrupt temperature changes. • Helps control the world’s climate.
Water is Less Dense as a Solid • Ice is less denseas a solid than as a liquid (ice floats)
Expansion When Frozen • Ice has a lower density than liquid water. Thus, ice floats on water. Helps keep the lake from freezing solid and forms an insulating barrier.
Universal Solvent • Water can dissolve a wide variety of compounds. • This means it can easily become polluted by water-soluble wastes.
The Properties of WaterQuestions • http://kisdwebs.katyisd.org/campuses/MRHS/teacherweb/hallk/Teacher%20Documents/AP%20Biology%20Materials/Chemistry%20of%20Life/The%20Properties%20of%20Water/02_A02s.swf
Temperatures around large bodies of water tend to be more moderate than temperatures inland. What property of water accounts for this? • A)Water has low salinity • B)Water has higher density than solvents • C)Water has the ability to absorb, store, and released large amounts of thermal energy • D)Water has polar properties that cause cohesion among individual water molecules.
Water has unique property. Like most liquids, it becomes denser as it cools, but at 4˚C it reaches maximum density. Solid ice is less dense than liquid water, which is why ice floats. How does this property protect aquatic life? • A) It keeps out predators • B) It keeps oxygen in the water • C) It conducts heat away from the lake • D) It helps keep lakes from freezing solid.
What accounts for many of the unique properties of water that make it essential for life? • Covalent bonds between hydrogen atoms in water molecules • Ionic bonds between water ions and other elements • Covalent bonds between water molecules • Polarity of water molecules.
The Gulf Stream is an ocean current that flows along Florida’s east coast. It has an important moderations effect on the climates of northern latitudes. Particularly in Greenland, Canada and Europe. What property of water makes the climate of these areas milder that they would otherwise be? • Melting point • Ability of water to moderate temperature • Polarity and electro negativity • Expansion of crystal structures as water freezes
Water is a common cleaning agent. It is most effective for the dissolving substances with which characteristic? • Polar bonds • High density • Nonelectolytes • Low electronegativity
Water is essential for life. Its special properties make water the single most important molecule in plant life. Which of the following properties of water enables it to move from the roots to the leaves of the plants? • Water expands as it freezes • Water is an excellent solvent • Water exhibits capillary action • Water is able to moderate temperature
Citrus trees can be damaged or even killed if temperatures stay below freezing long enough. On very cold winter nights in Florida, the citrus growers turn on the irrigation systems in the grooves to spray water on the trees, which forms a coat of ice on them. There are several reasons why this is helpful in protecting the trees. Which of the following is one of these reasons? • Water releases heat as it freezes • Ice protects the trees from wind chill • Water keeps the trees from dying out • Ice freezes the fruit so it won’t rot