Understanding C++ Programming Basics: Syntax, Semantics, and Control Structures
240 likes | 360 Vues
Learn the fundamental concepts of C++ programming including syntax templates, data types, declarations, variables, constants, and executable statements. Explore control structures like sequence, selection, looping, and subprograms while understanding the syntax and semantics of the language.

Understanding C++ Programming Basics: Syntax, Semantics, and Control Structures
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Syntax and Semantics, and the Program Development Process Robert Reaves
Four Basic Control Structures? • Sequence • Selection (branch) • Looping (repetition) • Subprogram (function)
Program Main function Square function Cube function
C++ Program Structure • Every C++ program must have a function named main. • Always begins with the first statement of main. • The body of a function is the statements between the ({) and (}). • Master(main) -> Servants(functions)
Value-Returning Functions • Square and Cube are both value-returning functions. • Returns a single value to it’s caller. • How do we know what the function returns? • Who calls main?
Main Function • Required function. • Execution begins here. • Returns a value to the OS.
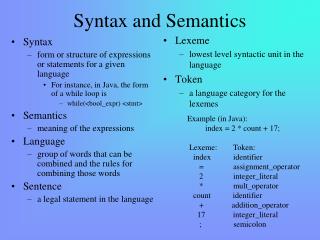
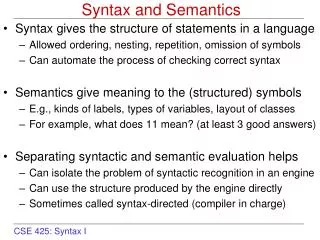
Syntax and Semantics • Programming language is a set of rules, symbols, and special words used to construct a program. • Syntax is formal rules governing how valid instructions are written in a programming language. • Semantics is the set of rules that determines the meaning of instructions written in a programming language. • Metalanguageis a language that is used to write syntax rules for another language.
Syntax Templates • Identifier is a name associated with a function or data object and used to refer to that function or data object. • Made up of letters (A-Z, a-z), digits (0-9), and or the underscore character (_). • Must being with a letter or underscore.
Identifiers (valid) • sum_of_squares • J9 • Box_22A • Bin3D4 • count
Identifiers (invalid) • 40Hours • Get Data • box-22 • cost_in_$ • int
Reserved Words • Reserved word is a word that has special meaning in C++; it cannot be used as a programmer-defined identifier. • Example: • int • char • return • for • const
Data Types • Data type a specific set of data values, along with a set of operations on those values. • Each piece of data must be a specific data type. • Determines how the data is represented in the computer and the kinds of processing the computer can perform on it. • Can define your own data types. (programmer-defined types)
Char Data Type • char describes data consisting of one alphanumeric character. (letter, digit, or special symbol) • Example: • ‘A’ • ‘1’ • ‘&’ • Each character must be enclosed in single quotes.
String Data Type • String is a sequence of characters, such as a word, name, or sentence, enclosed in double quotes. • Example: • “Hello, World!” • “Robert” • “Today is going to be a LONG class. =)” • What is a string containing no characters? • Not supplied by the C++ standard library.
Declarations • Identifiers can be used to name both constants and variables. • How do we tell the computer what an identifier represents? • Declaration a statement that associates an identifier with a data object, a function, or a data type so that the programmer can refer to that item by name. • Example: • int year;
Data Objects • Constants and variables collectively are called data objects.
Variables • A program operates on data, which is stored in memory. • Variable a location in memory referenced by an identifier, that contains a data value that can be changed. • Symbolic name associated with memory location is the variable name or variable identifier. • Declaring a variable means specifying both the variable’s name and its data type.
Variable Identifier myChar(memory location 1101010011) p Variable (char) Data Type Value
Constants • Constant is something whose value never changes. • Literal value any constant value written in a program. • Named Constant (symbolic constant) a location in memory, referenced by an identifier, that contains a data value that cannot be changed. • constDataType Identifier = LiteralValue;
Executable Statements • Assignment statement a statement that stores the value of an expression into a variable. • Expression an arrangement of identifiers, literals, and operators that can be evaluated to compute a value of a given type. • lastName = “Reaves”; • (=) what does the meaning of this operator mean?
String Expressions • Can’t perform arithmetic on strings, however you can use the (+) operator to perform something called concatenation. • Result of concatenating two strings is a new string containing the characters from both strings.
Output • Can write out values or variables and expressions by using a special variable named coutalong with the insertion operator (<<). • Displays on the standard output device, usually the display screen. • Coutis predefined in C++ systems to denote an output stream. • What is we want (“) is our output? • How do we terminate an output line?
Comments • Denoted by (//) or (/* */) • Single line or block comments • Ignored by the compiler • Can appear anywhere but in the middle of an identifier, a reserved word, or a literal constant. • You must use them or your coworkers and classmates will develop a seething hatred for you. • Failure to use proper comments is grounds for execution.