Endosymbiosis
120 likes | 563 Vues
Endosymbiosis. Do Now: . Mitochondria & Chloroplasts: Descendents of Ancient Prokaryotes. Chloroplasts and mitochondria are responsible for photosynthesis and cellular respiration in eukaryotes. Mitochondrion. Chloroplasts. Endosymbiosis.

Endosymbiosis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Endosymbiosis Do Now:
Mitochondria & Chloroplasts: Descendents of Ancient Prokaryotes • Chloroplasts and mitochondria are responsible for photosynthesis and cellular respiration in eukaryotes. Mitochondrion Chloroplasts
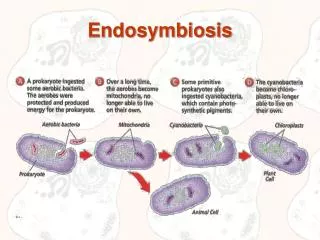
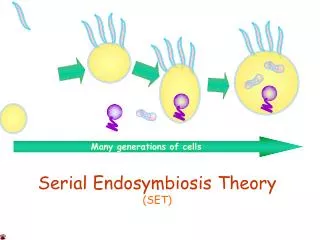
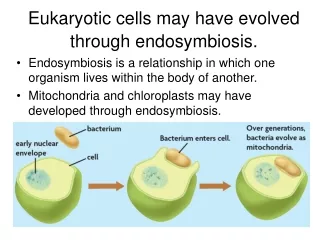
Endosymbiosis • Endosymbiosis: The theory that chloroplasts and mitochondria are descendents of ancient prokaryotes taken in by bigger cells during the process of evolution, leading to eukaryotic cells. • Evidence: • DNA: chloroplasts and mitochondria both contain their own genes, independent from nuclear DNA. • Reproduction: mitochondria and chloroplasts reproduce independently of the rest of the cell • Morphology: chloroplasts & mitochondria have double membranes – as would be expected if they were once engulfed. • Homology: mitochondria & chloroplasts share many similarities with known prokaryotes that exist today.
Eukaryotes without Mitochondria • They’re only a couple of examples, but they exist
Relatives? • Mitochondrial DNA is most similar to a group of aerobic heterotrophic bacteria, the alpha-proteobacteria. • Unsurprisingly, chloroplast DNA is most similar to that of cyannobacteria, the blue-green “algae.” • Over time, the genomes have changed, and they can no longer live outside of the cells in which they are found.
Watch the Movie • Though older, the movie shows some great cell biology, and presents good evidence for the endosymbiotic theory.
Maternal Inheritance: mtDNA • MtDNA is a useful tool for studying genetics and evolution, since it is not recombined during sexual reproduction • The Y-chromosome is similarly useful for studying patrilineal inheritance.
The Most Recent Matrilineal Common Ancestor. • Misleadingly referred to as mitochondrial Eve, this ancient woman is the most recent female ancestor all humans alive today have in common. • That’s right: the woman from whom you, myself, Michael Jackson, the Dali Lama, and EVERYONE else is descended. • She lived about 200,000 years ago in Africa, supported by both fossil and DNA evidence.